Green Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera Leaves and Its Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Activities
- PMID: 36193175
- PMCID: PMC9526645
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4136641
Green Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera Leaves and Its Antimicrobial and Cytotoxicity Activities
Abstract
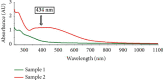
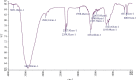
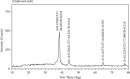
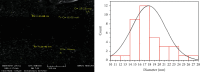
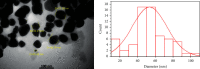
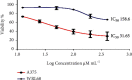
The plant occupied the largest area in the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles, especially the medicinal plants, and it has shown great potential in biotechnology applications. In this study, green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera leaves extract and its antifungal and antitumor activities were investigated. The formation of silver nanoparticles was observed after 1 hour of preparation color changing. The ultraviolet and visible spectrum, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy techniques were used to characterize synthesis particles. Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy showed a silver surface plasmon resonance band at 434 nm. Fourier transform infrared analysis shows the possible interactions between silver and bioactive molecules in Moringa oleifera leaves extracts, which may be responsible for the synthesis and stabilization of silver nanoparticles. X-ray diffraction showed that the particles were a semicubic crystal structure and with a size of 38.495 nm. Scanning electron microscopy imaging shows that the atoms are spherical in shape and the average size is 17 nm. The transmission electron microscopy image demonstrated that AgNPs were spherical and semispherical particles with an average of (50-60) nm. The nanoparticles also showed potent antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi using the well diffusion method. Candida glabrata found that the concentration of 1000 μg/mL exhibited the highest inhibition. As for bacteria, the concentration of 1000 μg/mL appeared to be the inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus. Moringa oleifera AgNPs inhibited human melanoma cells A375 line significant concentration-dependent cytotoxic effects. The powerful bioactivity of the green synthesized silver nanoparticles from medical plants recommends their biomedical use as antimicrobial as well as cytotoxic agents.
Copyright © 2022 Gufran Mahmood Mohammed and Sumaiya Naeema Hawar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Khan I., Saeed K., Khan I. Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian Journal of Chemistry . 2019;12(7):908–931. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011. - DOI
-
- Ying S., Guan Z., Ofpegbu P. C., et al. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: current development and limitations. Environmental Technology and Innovation Journal . 2022;26:1–20.
-
- Singh M., Prasad S., Gambihr I. S. Nanotechnology in medicine and antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticales. Digest journal of Nanomaterial and Biostrcture . 2008;3:115–122.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

