Bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle compromise due to hypoglycemic encephalopathy: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 36193280
- PMCID: PMC9525810
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.08.031
Bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle compromise due to hypoglycemic encephalopathy: A case report and literature review
Abstract
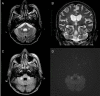
Hypoglycemic encephalopathy constitutes a critical presentation of severely diminished glucose levels. We present the case of a 53-year-old male patient with a history of diabetes mellitus with hypoglycemic encephalopathy and MRI findings of bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle lesions. Common findings of hypoglycemic encephalopathy described in the literature consist of bilateral compromise of the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, hippocampus, and long tracts of white matter. The cerebellum and brainstem are usually not affected. This is the ninth report of cerebellar peduncle compromise with hypoglycemia. As increasing evidence regarding prognosis estimation of lesion distribution arises, we consider it important to report the different cases of rare patterns of compromise.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Hypoglycemic encephalopathy; Middle cerebellar peduncle; Prognosis.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Sugimoto T, Morikawa Y, Ishikawa R, Abe T, Ohno N, Giga M, et al. MRI abnormality of the bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles and long-term follow-up in hypoglycemic encephalopathy: a case report. Neurol Clin Neurosci. 2021;9(1):130–133.
-
- Shirayama H, Ohshiro Y, Kinjo Y, Taira S, Teruya I, Nakachi K, et al. Acute brain injury in hypoglycemia induced hemiplegia. Diabet Med. 2004;21:623–624. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials