Harmful compounds of soy milk: characterization and reduction strategies
- PMID: 36193379
- PMCID: PMC9525506
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-021-05249-4
Harmful compounds of soy milk: characterization and reduction strategies
Abstract
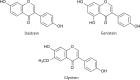
Soymilk is a plant based product which is a rich source of nutrients. However, various harmful compounds including allergens, anti-nutritional factors, and biogenic amines (BAs) exist in soybeans that may be transferred into soymilk. These compounds cause difficulties for consumers from mild to severe symptoms. Soymilk production is considered as a critical step in quantity of harmful compounds in final product. Common steps in soy milk manufacturing include soaking, grinding, and heating process. Allergens contents could be decreased by heating alone or in combination with structural modifiers and fermentation. BAs could be reduced by optimizing fermentation process and using suitable strains, especially BAs degradable types. Soaking, grinding and heating of soybeans in water are considered as effective methods for inactivation of antinutritional factors. Isoflavones are soy phytochemicals, which potentially leads to breast cancer in some women, can be converted to less bioavailable forms during processing. Other treatments such as high hydrostatic pressure and irradiation are also effective in harmful compounds reduction. Combination of the processes is more effective in harmful compounds removal. Considering the increasing trends in soymilk consumption, this review is focused on introduction of harmful compounds in soymilk and investigating the effects of processing condition on their concentration.
Keywords: Allergens; Anti-nutritional factors; Biogenic amines; Isoflavones; Soymilk.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Amnuaycheewa P, de Mejia EG. Purification, characterisation, and quantification of the soy allergen profilin (Gly m 3) in soy products. Food Chem. 2010;119(4):1671–2168. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.09.034. - DOI
-
- Ari M, Ayanwale B, Adama T, Olatunji E. Evaluation of the chemical composition and anti nutritional factors (ANFs) levels of different thermally processed soybeans. Asian J Agric Res. 2012;6(2):91–98.
-
- Biscola V, de Olmos AR, Choiset Y, Rabesona H, Garro MS, Mozzi F, Franco B. Soymilk fermentation by Enterococcus faecalis VB43 leads to reduction in the immunoreactivity of allergenic proteins β-conglycinin (7S) and glycinin (11S) Benef Microbes. 2017;8(4):635–643. doi: 10.3920/BM2016.0171. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources