Rare Variants in Genes Encoding Subunits of the Epithelial Na+ Channel Are Associated With Blood Pressure and Kidney Function
- PMID: 36193739
- PMCID: PMC9669116
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18513
Rare Variants in Genes Encoding Subunits of the Epithelial Na+ Channel Are Associated With Blood Pressure and Kidney Function
Abstract
Background: The epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) is intrinsically linked to fluid volume homeostasis and blood pressure. Specific rare mutations in SCNN1A, SCNN1B, and SCNN1G, genes encoding the α, β, and γ subunits of ENaC, respectively, are associated with extreme blood pressure phenotypes. No associations between blood pressure and SCNN1D, which encodes the δ subunit of ENaC, have been reported. A small number of sequence variants in ENaC subunits have been reported to affect functional transport in vitro or blood pressure. The effects of the vast majority of rare and low-frequency ENaC variants on blood pressure are not known.
Methods: We explored the association of low frequency and rare variants in the genes encoding ENaC subunits, with systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and pulse pressure. Using whole-genome sequencing data from 14 studies participating in the Trans-Omics in Precision Medicine Whole-Genome Sequencing Program, and sequence kernel association tests.
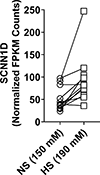
Results: We found that variants in SCNN1A and SCNN1B were associated with diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure (P<0.00625). Although SCNN1D is poorly expressed in human kidney tissue, SCNN1D variants were associated with systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and pulse pressure (P<0.00625). ENaC variants in 2 of the 4 subunits (SCNN1B and SCNN1D) were also associated with estimated glomerular filtration rate (P<0.00625), but not with stroke.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that variants in extrarenal ENaCs, in addition to ENaCs expressed in kidneys, influence blood pressure and kidney function.
Keywords: ENaC (epithelial Na+ channel); arterial pressure; blood pressure; glomerular filtration rate; kidney; stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resequencing Epithelial Sodium Channel Genes Identifies Rare Variants Associated With Blood Pressure Salt-Sensitivity: The GenSalt Study.Am J Hypertens. 2018 Jan 12;31(2):205-211. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpx169. Am J Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 29036630 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) family: Phylogeny, structure-function, tissue distribution, and associated inherited diseases.Gene. 2016 Apr 1;579(2):95-132. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.12.061. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26772908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis of Rwandan patients with cystic fibrosis-like symptoms: identification of novel cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and epithelial sodium channel gene variants.Chest. 2009 May;135(5):1233-1242. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-2246. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Chest. 2009. PMID: 19017867
-
Use of constant denaturant capillary electrophoresis of pooled blood samples to identify single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes (Scnn1a and Scnn1b) encoding the alpha and beta subunits of the epithelial sodium channel.Clin Chem. 2002 May;48(5):718-28. Clin Chem. 2002. PMID: 11978598
-
The epithelial sodium channel in inflammation and blood pressure modulation.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr 12;10:1130148. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1130148. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37123470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Eicosanoid-Regulated Myeloid ENaC and Isolevuglandin Formation in Human Salt-Sensitive Hypertension.Hypertension. 2024 Mar;81(3):516-529. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.21285. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Hypertension. 2024. PMID: 37675576 Free PMC article.
-
SECS, drugs, and Rac1&Rho: regulation of EnNaC in vascular endothelial cells.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Jul;477(7):977-992. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03093-5. Epub 2025 May 22. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 40402207 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and oxidative stress in salt sensitive hypertension; The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome.Front Physiol. 2022 Dec 22;13:1096296. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1096296. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36620210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic cell epithelial sodium channel induced inflammation and salt-sensitive hypertension.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2024 Mar 1;33(2):145-153. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000963. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38180118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial and seasonal groundwater quality assessment for drinking suitability using index and machine learning approach.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 27;10(9):e30362. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30362. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38742059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu JJ, Elkaddi N, Garcia-Blanco A, Spielman AI, Bachmanov AA, Chung HY, Ozdener MH. Arginyl dipeptides increase the frequency of NaCl-elicited responses via epithelial sodium channel alpha and delta subunits in cultured human fungiform taste papillae cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:7483. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07756-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NR002241/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL144941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072518/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL155041/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK061296/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090682/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL130497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055673/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112064/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133040/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087698/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL046380/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125439/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG011052/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL049762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK063922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087263/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

