Rare Variants in Genes Encoding Subunits of the Epithelial Na+ Channel Are Associated With Blood Pressure and Kidney Function
- PMID: 36193739
- PMCID: PMC9669116
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18513
Rare Variants in Genes Encoding Subunits of the Epithelial Na+ Channel Are Associated With Blood Pressure and Kidney Function
Abstract
Background: The epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) is intrinsically linked to fluid volume homeostasis and blood pressure. Specific rare mutations in SCNN1A, SCNN1B, and SCNN1G, genes encoding the α, β, and γ subunits of ENaC, respectively, are associated with extreme blood pressure phenotypes. No associations between blood pressure and SCNN1D, which encodes the δ subunit of ENaC, have been reported. A small number of sequence variants in ENaC subunits have been reported to affect functional transport in vitro or blood pressure. The effects of the vast majority of rare and low-frequency ENaC variants on blood pressure are not known.
Methods: We explored the association of low frequency and rare variants in the genes encoding ENaC subunits, with systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and pulse pressure. Using whole-genome sequencing data from 14 studies participating in the Trans-Omics in Precision Medicine Whole-Genome Sequencing Program, and sequence kernel association tests.
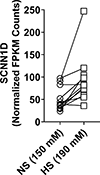
Results: We found that variants in SCNN1A and SCNN1B were associated with diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure (P<0.00625). Although SCNN1D is poorly expressed in human kidney tissue, SCNN1D variants were associated with systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and pulse pressure (P<0.00625). ENaC variants in 2 of the 4 subunits (SCNN1B and SCNN1D) were also associated with estimated glomerular filtration rate (P<0.00625), but not with stroke.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that variants in extrarenal ENaCs, in addition to ENaCs expressed in kidneys, influence blood pressure and kidney function.
Keywords: ENaC (epithelial Na+ channel); arterial pressure; blood pressure; glomerular filtration rate; kidney; stroke.
Figures
References
-
- Xu JJ, Elkaddi N, Garcia-Blanco A, Spielman AI, Bachmanov AA, Chung HY, Ozdener MH. Arginyl dipeptides increase the frequency of NaCl-elicited responses via epithelial sodium channel alpha and delta subunits in cultured human fungiform taste papillae cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:7483. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07756-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NR002241/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL144941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072518/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL155041/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK061296/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090682/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL130497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055673/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112064/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133040/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087698/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL046380/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125439/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG011052/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL049762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK063922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087263/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

