The Neurodata Without Borders ecosystem for neurophysiological data science
- PMID: 36193886
- PMCID: PMC9531949
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.78362
The Neurodata Without Borders ecosystem for neurophysiological data science
Abstract
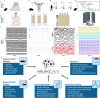
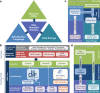
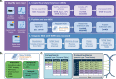
The neurophysiology of cells and tissues are monitored electrophysiologically and optically in diverse experiments and species, ranging from flies to humans. Understanding the brain requires integration of data across this diversity, and thus these data must be findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). This requires a standard language for data and metadata that can coevolve with neuroscience. We describe design and implementation principles for a language for neurophysiology data. Our open-source software (Neurodata Without Borders, NWB) defines and modularizes the interdependent, yet separable, components of a data language. We demonstrate NWB's impact through unified description of neurophysiology data across diverse modalities and species. NWB exists in an ecosystem, which includes data management, analysis, visualization, and archive tools. Thus, the NWB data language enables reproduction, interchange, and reuse of diverse neurophysiology data. More broadly, the design principles of NWB are generally applicable to enhance discovery across biology through data FAIRness.
Keywords: FAIR data; Neurophysiology; archive; data ecosystem; data language; data standard; human; mouse; neuroscience; rat.
Plain language summary
The brain is an immensely complex organ which regulates many of the behaviors that animals need to survive. To understand how the brain works, scientists monitor and record brain activity under different conditions using a variety of experimental techniques. These neurophysiological studies are often conducted on multiple types of cells in the brain as well as a variety of species, ranging from mice to flies, or even frogs and worms. Such a range of approaches provides us with highly informative, complementary ‘views’ of the brain. However, to form a complete, coherent picture of how the brain works, scientists need to be able to integrate all the data from these different experiments. For this to happen effectively, neurophysiology data need to meet certain criteria: namely, they must be findable, accessible, interoperable, and re-usable (or FAIR for short). However, the sheer diversity of neurophysiology experiments impedes the ‘FAIR’-ness of the information obtained from them. To overcome this problem, researchers need a standardized way to communicate their experiments and share their results – in other words, a ‘standard language’ to describe neurophysiology data. Rübel, Tritt, Ly, Dichter, Ghosh et al. therefore set out to create such a language that was not only FAIR, but could also co-evolve with neurophysiology research. First, they produced a computer software program (called Neurodata Without Borders, or NWB for short) which generated and defined the different components of the new standard language. Then, other tools for data management were created to expand the NWB platform using the standardized language. This included data analysis and visualization methods, as well as an ‘archive’ to store and access data. Testing the new language and associated tools showed that they indeed allowed researchers to access, analyze, and share information from many different types of experiments, in organisms ranging from flies to humans. The NWB software is open-source, meaning that anyone can obtain a copy and make changes to it. Thus, NWB and its associated resources provide the basis for a collaborative, community-based system for sharing neurophysiology data. Rübel et al. hope that NWB will inspire similar developments across other fields of biology that share similar levels of complexity with neurophysiology.
© 2022, Rübel, Tritt, Ly et al.
Conflict of interest statement
OR, AT, RL, SG, PB, IS, LN, KS, LF, KB No competing interests declared, BD BD is the Founder and CEO of CatalystNeuro, a software consulting company that works with neurophysiology labs to build state-of-the-art data management workflows. Much of this work involves converting data from lab-specific formats to the NWB standard, and enhancing analysis and visualization tools to read and write NWB data. As such, Dr. Dichter has a personal financial state in the success of the NWB standard, LN LN is a software engineer at MBF Bioscience, a for-profit biotech company that develops microscopy software and hardware
Figures




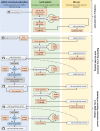



References
-
- Ahanonu B. calciumImagingAnalysis (ciapkg): a software package for analyzing one- and two-photon calcium imaging datasets. Zenodo. 2018 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.2222295. - DOI
-
- Bargmann C. BRAIN 2025: a scientific vision. BRAIN Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Working Group Report to the Advisory Committee to the Director, NIH 2014
-
- Bouchard KE, Aimone JB, Chun M, Dean T, Denker M, Diesmann M, Donofrio DD, Frank LM, Kasthuri N, Koch C, Ruebel O, Simon HD, Sommer FT. High-performance computing in neuroscience for data-driven discovery, integration, and dissemination. Neuron. 2016;92:628–631. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.10.035. - DOI - PubMed

