Rational Design of Chitin Deacetylase Inhibitors for Sustainable Agricultural Use Based on Molecular Topology
- PMID: 36194443
- PMCID: PMC10389753
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c02377
Rational Design of Chitin Deacetylase Inhibitors for Sustainable Agricultural Use Based on Molecular Topology
Abstract
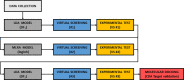
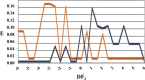
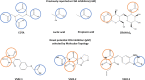
Fungicide resistance is a major concern in modern agriculture; therefore, there is a pressing demand to develop new, greener chemicals. Chitin is a major component of the fungal cell wall and a well-known elicitor of plant immunity. To overcome chitin recognition, fungal pathogens developed different strategies, with chitin deacetylase (CDA) activity being the most conserved. This enzyme is responsible for hydrolyzing the N-acetamido group in N-acetylglucosamine units of chitin to convert it to chitosan, a compound that can no longer be recognized by the plant. In previous works, we observed that treatments with CDA inhibitors, such as carboxylic acids, reduced the symptoms of cucurbit powdery mildew and induced rapid activation of chitin-triggered immunity, indicating that CDA could be an interesting target for fungicide development. In this work, we developed an in silico strategy based on QSAR (quantitative structure-activity relationship) and molecular topology (MT) to discover new, specific, and potent CAD inhibitors. Starting with the chemical structures of few carboxylic acids, with and without disease control activity, three predictive equations based on the MT paradigm were developed to identify a group of potential molecules. Their fungicidal activity was experimentally tested, and their specificity as CDA inhibitors was studied for the three best candidates by molecular docking simulations. To our knowledge, this is the first time that MT has been used for the identification of potential CDA inhibitors to be used against resistant powdery mildew strains. In this sense, we consider of special interest the discovery of molecules capable of stimulating the immune system of plants by triggering a defensive response against fungal species that are highly resistant to fungicides such as powdery mildew.
Keywords: QSAR; crop protection; fungicide resistance; molecular topology; pest control; pesticide design; powdery mildew.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Suppression of Chitin-Triggered Immunity by Plant Fungal Pathogens: A Case Study of the Cucurbit Powdery Mildew Fungus Podosphaera xanthii.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;9(7):771. doi: 10.3390/jof9070771. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Design of a Potential New Nematicide Targeting Chitin Deacetylase.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Feb 7;72(5):2482-2491. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05258. Epub 2024 Jan 24. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38264997 Free PMC article.
-
Chitin Deacetylase, a Novel Target for the Design of Agricultural Fungicides.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;7(12):1009. doi: 10.3390/jof7121009. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946992 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Chitin-Triggered Immunity by a New Fungal Chitin-Binding Effector Resulting from Alternative Splicing of a Chitin Deacetylase Gene.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;8(10):1022. doi: 10.3390/jof8101022. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36294587 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan in plant protection.Mar Drugs. 2010 Mar 30;8(4):968-87. doi: 10.3390/md8040968. Mar Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20479963 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of Chitin-Triggered Immunity by Plant Fungal Pathogens: A Case Study of the Cucurbit Powdery Mildew Fungus Podosphaera xanthii.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;9(7):771. doi: 10.3390/jof9070771. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Design of a Potential New Nematicide Targeting Chitin Deacetylase.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Feb 7;72(5):2482-2491. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05258. Epub 2024 Jan 24. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38264997 Free PMC article.
-
Salicylic Acid Mediates Chitosan-Induced Immune Responses and Growth Enhancement in Barley.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 10;25(24):13244. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413244. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769012 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting bacterial growth in biofilm conditions: rational design of novel inhibitors to mitigate clinical and food contamination using QSAR.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024 Dec;39(1):2330907. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2330907. Epub 2024 Apr 23. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38651823 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular structure, biological roles, and inhibition of plant pathogenic fungal chitin deacetylases.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 9;14:1335646. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1335646. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38264029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fernández-Ortuño D.; Pérez-García A.; López-Ruiz F.; Romero D.; de Vicente A.; Torés J. A. Occurrence and distribution of resistance to QoI fungicides in populations of Podosphaera fusca in south central Spain. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 115, 215–222. 10.1007/s10658-006-9014-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

