Electroacupuncture reduces blood glucose by regulating intestinal flora in type 2 diabetic mice
- PMID: 36195536
- PMCID: PMC9574722
- DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13323
Electroacupuncture reduces blood glucose by regulating intestinal flora in type 2 diabetic mice
Abstract
Background: The development of diabetes is closely related to the gut microbiota in recent studies, which can be influenced by intestinal motility. A few studies report that electroacupuncture (EA) can lower blood glucose. EA can promote colonic motility and influence gut microbes. In this study, we explored the effect of the EA on blood glucose level in mice with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and its mechanism.
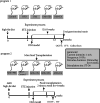
Methods: The T2D mice model, fecal microbiota transplantation mice model, and KitW/Wv mice model (Point mutation of mouse W locus encoding kit gene)were used to investigate the effect of EA on blood glucose as well as the mechanism; The blood glucose and insulin resistance level and the intestinal flora were evaluated. The level of intestinal junction protein, inflammatory cytokines in the serum, interstitial cells of Cajal content, and colonic motility were detected. Lastly, the IKKβ/NF-κB-JNK-IRS-1-AKT pathway was explored.
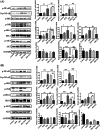
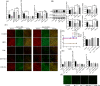
Results: EA lowered the blood glucose level, altered the gut microbiota, and promoted colonic motility in T2D mice. EA-altered microbiota decreased the blood glucose level and insulin resistance in the antibiotics-treated diabetic mice. EA increased tight junction protein, lowered inflammatory factors, and regulated the IKKβ/NF-κB-JNK-IRS-1-AKT pathway in the liver and muscles. EA could not reduce the blood glucose and regulated gut microbiota in the KitW/Wv mice model.
Conclusions: EA promoted intestinal motility to regulate the intestinal flora, thereby reducing the level of systemic inflammation, and ultimately lowering the blood glucose by the IKKβ/NF-κB-JNK-IRS-1-AKT signal pathway.
背景: 最近的研究表明, 糖尿病的发展与肠道菌群密切相关, 肠道菌群可能会受到肠道运动的影响。一些文献报道电针(EA)可以降低血糖。 EA可以促进结肠运动并影响肠道微生物。在这项研究中, 我们探讨了 EA 对 2 型糖尿病 (T2D) 小鼠血糖水平的影响及其机制。 方法: 采用T2D小鼠模型、FMT(粪菌移植)小鼠模型和KitW/Wv 小鼠模型, 研究电针对血糖的影响及其作用机制, 评估血糖和胰岛素抵抗水平以及肠道菌群。检测肠连接蛋白水平、血清和结肠炎性细胞因子水平、ICC(Cajal间质细胞)含量及结肠运动性。最后, 探索了 IKKβ/NF-κB-JNK-IRS-1-AKT 通路。 结果: 1. EA降低了T2D小鼠的血糖水平, 改变了肠道菌群, 促进了结肠运动。 2. EA 改变的微生物群降低了 ABX(抗生素)治疗的糖尿病小鼠的血糖水平和胰岛素抵抗。 3. EA增加紧密连接蛋白, 降低炎症因子, 并调节肝脏和肌肉中的IKKβ/NF-κB-JNK-IRS-1-AKT通路。 4. EA不能降低KitW/Wv 小鼠模型中的血糖和调节肠道菌群。 结论: 电针通过IKKβ/NF-κBJNK-IRS-1-AKT信号通路促进肠道运动, 调节肠道菌群, 从而降低全身炎症水平, 最终降低血糖。.
Keywords: 2型糖尿病; ICC; electroacupuncture; gut microbiota; inflammation; type 2 diabetes; 炎症; 电针; 肠道菌群.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes published by Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai JiaoTong University School of Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Mechanisms of electroacupuncture in improving obesity-induced insulin resistance via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway in liver].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Jun 25;47(6):504-9. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210362. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35764517 Chinese.
-
Electroacupuncture promotes the gastrointestinal motility of diabetic mice by CNP/NPR-B-cGMP and PDE3A-cGMP signaling.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019 Apr;31(4):e13539. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13539. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019. PMID: 30672071
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture combined with Zhuang-medicine-thread moxibustion on silent information regulator-1/nuclear factor κB signaling pathway in gastric antrum of diabetic gastroparesis rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Oct 25;46(10):837-44. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200942. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34698457 Chinese.
-
Exploring Mechanism of Electroacupuncture in Modulating Neuroinflammation Based on Intestinal Flora and Its Metabolites.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Feb;31(2):183-192. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3766-9. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 39039343 Review.
-
Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and insulin sensitivity.Nutr Res Rev. 2018 Jun;31(1):35-51. doi: 10.1017/S095442241700018X. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Nutr Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29037268 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomics Analysis of the Mechanism of Yuquan Capsules in the Treatment of T2DM Rats Using UPLC/MS.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Mar 27;18:905-916. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S512089. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40165883 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac energy metabolic disorder and gut microbiota imbalance: a study on the therapeutic potential of Shenfu Injection in rats with heart failure.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 25;16:1509548. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1509548. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40071211 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acupuncture on the insulin signaling pathway and mitochondrial AMPK pathway in an animal model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic evaluation and meta-analysis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 May 2;17(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01634-7. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40312379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via the Regulation of Gut Microbiota: A Chinese Medicine Perspective.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 18;16(22):3935. doi: 10.3390/nu16223935. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture and Drug Combination Therapy for Abnormal Glucose Metabolism: Exploring Synergistic Enhancement and Reduced Toxicity Mechanisms.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Nov 28;17:4525-4537. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S492626. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39624791 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ishizaki N, Okushi N, Yano T, Yamamura Y. Improvement in glucose tolerance as a result of enhanced insulin sensitivity during electroacupuncture in spontaneously diabetic Goto‐Kakizaki rats. Metabolism. 2009;58(10):1372‐1378. - PubMed
-
- Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, et al. A metagenome‐wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2012;490(7418):55‐60. - PubMed
-
- Cotillard A, Kennedy SP, Kong LC, et al. Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature. 2013;500(7464):585‐588. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

