Therapeutic Reference Range for Aripiprazole in Schizophrenia Revised: a Systematic Review and Metaanalysis
- PMID: 36195732
- PMCID: PMC9584998
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-022-06233-2
Therapeutic Reference Range for Aripiprazole in Schizophrenia Revised: a Systematic Review and Metaanalysis
Abstract
Rationale: While one of the basic axioms of pharmacology postulates that there is a relationship between the concentration and effects of a drug, the value of measuring blood levels is questioned by many clinicians. This is due to the often-missing validation of therapeutic reference ranges.
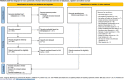
Objectives: Here, we present a prototypical meta-analysis of the relationships between blood levels of aripiprazole, its target engagement in the human brain, and clinical effects and side effects in patients with schizophrenia and related disorders.
Methods: The relevant literature was systematically searched and reviewed for aripiprazole oral and injectable formulations. Population-based concentration ranges were computed (N = 3,373) and pharmacokinetic influences investigated.
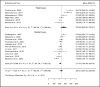
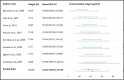
Results: Fifty-three study cohorts met the eligibility criteria. Twenty-nine studies report blood level after oral, 15 after injectable formulations, and nine were positron emission tomography studies. Conflicting evidence for a relationship between concentration, efficacy, and side effects exists (assigned level of evidence low, C; and absent, D). Population-based reference ranges are well in-line with findings from neuroimaging data and individual efficacy studies. We suggest a therapeutic reference range of 120-270 ng/ml and 180-380 ng/ml, respectively, for aripiprazole and its active moiety for the treatment of schizophrenia and related disorders.
Conclusions: High interindividual variability and the influence of CYP2D6 genotypes gives a special indication for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of oral and long-acting aripiprazole. A starting dose of 10 mg will in most patients result in effective concentrations in blood and brain. 5 mg will be sufficient for known poor metabolizers.
Keywords: Adverse drug reaction; Aripiprazole; Blood level; Clinical effects; Dopamine receptor occupancy; Reference range; Therapeutic Drug Monitoring.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. GG has served as a consultant for Allergan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Recordati, Roche, ROVI, Sage, and Takeda. He has served on the speakers’ bureau of Gedeon Richter, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, and Recordati. He has received grant support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Lundbeck, and Saladax. He is co-founder and/or shareholder of Mind and Brain Institute GmbH, Brainfoods GmbH, OVID Health Systems GmbH and MIND Foundation gGmbH. CH has served on the speakers’ bureau of Otsuka. GS has served as a consultant and has received speaker fees from HLS Therapeutics. MP has received speaker’s fees from Janssen, ROVI, Neuraxpharm, Lundbeck, and Otsuka. He has served as a consultant for Novartis, Otsuka, and ROVI. MP is an editor of an internet-based drug–drug interaction program (
Figures

References
-
- Egberts K, Reuter-Dang SY, Fekete S, Kulpok C, Mehler-Wex C, Wewetzer C, Karwautz A, Mitterer M, Holtkamp K, Boege I, Burger R, Romanos M, Gerlach M, Taurines R. Therapeutic drug monitoring of children and adolescents treated with aripiprazole: observational results from routine patient care. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2020;127(12):1663–1674. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02253-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

