Long-range phasing of dynamic, tissue-specific and allele-specific regulatory elements
- PMID: 36195755
- PMCID: PMC10567064
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01188-8
Long-range phasing of dynamic, tissue-specific and allele-specific regulatory elements
Abstract
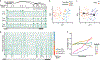
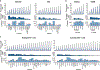
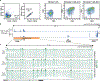
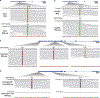
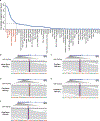
Epigenomic maps identify gene regulatory elements by their chromatin state. However, prevailing short-read sequencing methods cannot effectively distinguish alleles, evaluate the interdependence of elements in a locus or capture single-molecule dynamics. Here, we apply targeted nanopore sequencing to profile chromatin accessibility and DNA methylation on contiguous ~100-kb DNA molecules that span loci relevant to development, immunity and imprinting. We detect promoters, enhancers, insulators and transcription factor footprints on single molecules based on exogenous GpC methylation. We infer relationships among dynamic elements within immune loci, and order successive remodeling events during T cell stimulation. Finally, we phase primary sequence and regulatory elements across the H19/IGF2 locus, uncovering primate-specific features. These include a segmental duplication that stabilizes the imprinting control region and a noncanonical enhancer that drives biallelic IGF2 expression in specific contexts. Our study advances emerging strategies for phasing gene regulatory landscapes and reveals a mechanism that overrides IGF2 imprinting in human cells.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest
B.E.B. declares outside interests in Fulcrum Therapeutics, Arsenal Biosciences, HiFiBio, Cell Signaling Technologies and Chroma Medicine. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




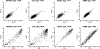


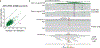


References
-
- Greenberg MVC & Bourc’his D The diverse roles of DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 20, 590–607 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Lappalainen T & Greally JM Associating cellular epigenetic models with human phenotypes. Nat. Rev. Genet 18, 441–451 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Cavalli G & Heard E Advances in epigenetics link genetics to the environment and disease. Nature 571, 489–499 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Klemm SL, Shipony Z & Greenleaf WJ Chromatin accessibility and the regulatory epigenome. Nat. Rev. Genet 20, 207–220 (2019). - PubMed
Methods-only references
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

