lncRNA PVT1: a novel oncogene in multiple cancers
- PMID: 36195846
- PMCID: PMC9533616
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-022-00385-x
lncRNA PVT1: a novel oncogene in multiple cancers
Abstract
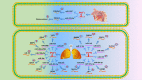
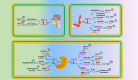
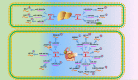
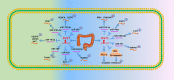
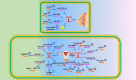
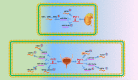
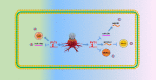
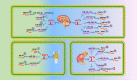
Long noncoding RNAs are involved in epigenetic gene modification, including binding to the chromatin rearrangement complex in pre-transcriptional regulation and to gene promoters in gene expression regulation, as well as acting as microRNA sponges to control messenger RNA levels in post-transcriptional regulation. An increasing number of studies have found that long noncoding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) plays an important role in cancer development. In this review of a large number of studies on PVT1, we found that PVT1 is closely related to tumor onset, proliferation, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transformation, and apoptosis, as well as poor prognosis and radiotherapy and chemotherapy resistance in some cancers. This review comprehensively describes PVT1 expression in various cancers and presents novel approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; Long noncoding RNA; Oncogene; PVT1.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

