Deeper insight into the role of IL-17 in the relationship beween hypertension and intestinal physiology
- PMID: 36195874
- PMCID: PMC9530412
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-022-00311-0
Deeper insight into the role of IL-17 in the relationship beween hypertension and intestinal physiology
Abstract
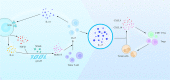
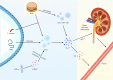
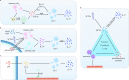
With the incidence of hypertension increasing worldwide, more and more the mechanisms of hypertension from the perspective of immunity have found. Intestinal microbiota as well as its metabolites relationship with hypertension has attracted great attention from both clinicians and investigators. However, the associations of hypertension with lesions of a large number of immune factors including IL-17, MCP-1, IL-6, TGF-β, IL-10 and others have not been fully characterized. In this review, after introducing the immune factors as the most potent anti/pro-hypertension agents known, we provide detailed descriptions of the IL-17 involved in the pathology of hypertension, pointing out the underlying mechanisms and suggesting the clinical indications.
Keywords: Gut microbiota; Hypertension; IL-10; IL-17; IL-6; Immune factors; MCP-1; TGF-β.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Umbilical Mesenchymal Stem Cells Display Therapeutic Potential in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating Interactions Between Immunity and Gut Microbiota via the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Mar 13;8:131. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00131. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32232043 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma cytokine levels in patients with chronic alcohol overconsumption: Relations to gut microbiota markers and clinical correlates.Alcohol. 2020 Jun;85:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.10.002. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Alcohol. 2020. PMID: 31610228
-
Insight into the Role of Psychological Factors in Oral Mucosa Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 26;23(9):4760. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094760. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of diet on hypertensive pathology: is there a link via gut microbiota-driven immunometabolism?Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Jul 1;115(9):1435-1447. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz091. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30951169 Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Gut Dysbiosis in Cardio-metabolic Risk Factors for Heart Failure.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020 May 8;22(5):38. doi: 10.1007/s11906-020-01046-0. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020. PMID: 32385705 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota and hypertension: a bibliometric analysis of recent research (2014-2023).Front Nutr. 2023 Oct 12;10:1253803. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1253803. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37899834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the mechanism of acupuncture to improve mild cognitive impairment in hypertension by regulating intestinal microbiome.Front Neurosci. 2024 Dec 23;18:1495384. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1495384. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39764388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota dependant trimethylamine N-oxide and hypertension.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1075641. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1075641. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37089429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

