Effectiveness and Tolerability of Anlotinib Plus PD-1 Inhibitors for Patients with Previously Treated Metastatic Soft-Tissue Sarcoma
- PMID: 36196372
- PMCID: PMC9527032
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S379269
Effectiveness and Tolerability of Anlotinib Plus PD-1 Inhibitors for Patients with Previously Treated Metastatic Soft-Tissue Sarcoma
Abstract
Objective: This study was to investigate the effectiveness and tolerability of anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitors for patients with previously treated metastatic soft tissue sarcoma (STS).
Methods: Patients with previously treated metastatic STS who were administered with anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitors in clinical practice were included for analysis retrospectively. All the common subtypes of advanced STS were appropriate for analysis. Efficacy of the regimen was assessed according to the change of target lesion radiologically, and all the patients were followed up regularly. Safety profile during the combination administration was recorded and documented specifically. Clinical significance according to different STS subtypes was analyzed accordingly.
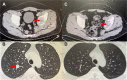
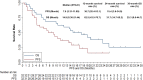
Results: From September 2018 to January 2022, a total of 32 patients with previously treated metastatic STS who received anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades were screened for the analysis in this study. The best overall response during the combination administration indicated that partial response was observed in 11 patients, stable disease was noted in 16 patients and progressive disease was found in 6 patients, yielding an objective response rate (ORR) of 34.4% (95% CI: 18.6-53.2%) and a disease control rate (DCR) of 84.4% (95% CI: 67.2-94.7%). Furthermore, the median PFS of 32 patients with metastatic STS was 7.6 months (95% CI: 3.31-11.89) and the median OS was 14.9 months (95% CI: 8.36-21.44). Besides, adverse reactions related to the treatment during anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitors administration were observed in 29 patients (90.6%), of whom, a total of 13 patients (40.6%) were deemed as grade 3-4 adverse reactions and no grade 5 adverse reaction was found. Specifically, the most common adverse reactions were fatigue, hypertension, hand-foot syndrome, diarrhea and dermal toxicity.
Conclusion: Anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitors demonstrated durable and promising efficacy and tolerable safety for patients with metastatic STS in real world. Further prospective clinical trials were warranted to validate the feasibility of anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades clinically.
Keywords: PD-1 inhibitors; anlotinib; effectiveness; soft tissue sarcoma; tolerability.
© 2022 Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades in Patients with Previously Immunotherapy Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study.Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2024 Mar 25;15:29-40. doi: 10.2147/LCTT.S444884. eCollection 2024. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 38560413 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and Tolerability of Anlotinib Plus PD-1 Blockades for Patients with Treatment-Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Feb 1;16:73-86. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S427680. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 38318097 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Activity and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades for Patients with Previously Treated Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Dec 30;14:10483-10493. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S337316. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 35002304 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety evaluations of anlotinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with bevacizumab.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 27;13:973448. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.973448. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36238567 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Jul;152:165-182. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.04.034. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34107450
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of anlotinib plus camrelizumab in treating retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcomas: a single-center retrospective cohort study.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Mar 15;11(5):212. doi: 10.21037/atm-23-460. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37007540 Free PMC article.
-
Anlotinib for the treatment of pulmonary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a case report.Anticancer Drugs. 2025 Sep 1;36(8):678-681. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001731. Epub 2025 May 12. Anticancer Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40353528 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab plus anlotinib hydrochloride in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the phase II OASIS trial.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 15;15(1):8876. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53109-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39406730 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Implication of PD‑L1 polymorphisms rs2297136 on clinical outcomes of patients with advanced NSCLC who received PD‑1 blockades: A retrospective exploratory study.Oncol Lett. 2024 Feb 7;27(4):144. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14277. eCollection 2024 Apr. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38385107 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades in Patients with Previously Immunotherapy Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study.Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2024 Mar 25;15:29-40. doi: 10.2147/LCTT.S444884. eCollection 2024. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 38560413 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

