CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2015-2019
- PMID: 36196752
- PMCID: PMC9533228
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noac202
CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2015-2019
Abstract
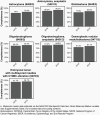
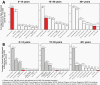
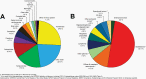
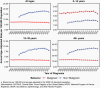
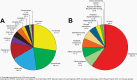
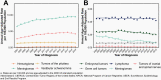
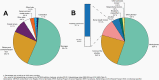
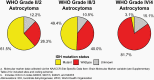
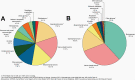
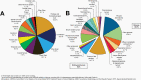
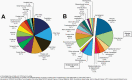
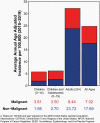
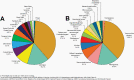
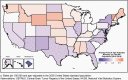
The Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States (CBTRUS), in collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Cancer Institute, is the largest population-based registry focused exclusively on primary brain and other central nervous system (CNS) tumors in the United States (US) and represents the entire US population. This report contains the most up-to-date population-based data on primary brain tumors available and supersedes all previous reports in terms of completeness and accuracy. All rates are age-adjusted using the 2000 US standard population and presented per 100,000 population. The average annual age-adjusted incidence rate (AAAIR) of all malignant and non-malignant brain and other CNS tumors was 24.71 per 100,000 population (malignant AAAIR=7.02 and non-malignant AAAIR=17.69). This overall rate was higher in females compared to males (27.62 versus 21.60 per 100,000) and non-Hispanic persons compared to Hispanic persons (25.09 versus 22.95 per 100,000). The most commonly occurring malignant brain and other CNS histopathology was glioblastoma (14.2% of all tumors and 50.1% of all malignant tumors), and the most common non-malignant histopathology was meningioma (39.7% of all tumors and 55.4% of all non-malignant tumors). Glioblastoma was more common in males, and meningiomas were more common in females. In children and adolescents (ages 0-19 years), the incidence rate of all primary brain and other CNS tumors was 6.20 per 100,000 population. An estimated 93,470 new cases of malignant and non-malignant brain and other CNS tumors are expected to be diagnosed in the US population in 2022 (26,670 malignant and 66,806 non-malignant). There were 84,264 deaths attributed to malignant brain and other CNS tumors between 2015 and 2019. This represents an average annual mortality rate of 4.41 per 100,000 population and an average of 16,853 deaths per year. The five-year relative survival rate following diagnosis of a malignant brain and other CNS tumor was 35.7%, while for non-malignant brain and other CNS tumors the five-year relative survival rate was 91.8%.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures












References
-
- Louis DN OH, Wiestler OD, Cavanee WK, ed WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2016.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Program of Cancer Registries Cancer Surveillance System Rationale and Approach. 1999; http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/npcr/pdf/npcr_css.pdf. Accessed July 21, 2020.
-
- Cancer Registries Amendment Act, 102nd Cong. § 515 (1992). https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/STATUTE-106/pdf/STATUTE-106-Pg3372.pdf. Accessed July 21, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

