pH Dependence of Amyloid-β Fibril Assembly Kinetics: Unravelling the Microscopic Molecular Processes
- PMID: 36197009
- PMCID: PMC9828734
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202210675
pH Dependence of Amyloid-β Fibril Assembly Kinetics: Unravelling the Microscopic Molecular Processes
Abstract
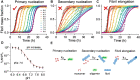
Central to Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the assembly of the amyloid-beta peptide (Aβ) into fibrils. A reduction in pH accompanying inflammation or subcellular compartments, may accelerate fibril formation as the pH approaches Aβ's isoelectric point (pI). Using global fitting of fibril formation kinetics over a range of pHs, we identify the impact net charge has on individual fibril assembly microscopic rate constants. We show that the primary nucleation has a strong pH dependence. The titration behaviour exhibits a mid-point or pKa of 7.0, close to the pKa of Aβ histidine imidazoles. Surprisingly, both the secondary nucleation and elongation rate constants are pH independent. This indicates the charge of Aβ, in particular histidine protonation, has little impact on this stage of Aβ assembly. These fundamental processes are key to understanding the forces that drive the assembly of Aβ into toxic oligomers and fibrils.
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease; Amyloid; Isoelectric Point; Kinetics; Molecular Mechanism.
© 2022 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Prince M., Wimo A., Guerchet M., Gemma-Claire A., Wu Y.-T., Prina M., Alzheimer's Disease Int. 2015, 1, 1–84.<
-
- None
-
- Scheuner D., Eckman C., Jensen M., Song X., Citron M., Suzuki N., Bird T. D., Hardy J., Hutton M., Kukull W., Larson E., LevyLahad E., Viitanen M., Peskind E., Poorkaj P., Schellenberg G., Tanzi R., Wasco W., Lannfelt L., Selkoe D., Younkin S., Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 864–870; - PubMed
-
- None
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

