Membrane compartmentalization of Ect2/Cyk4/Mklp1 and NuMA/dynein regulates cleavage furrow formation
- PMID: 36197340
- PMCID: PMC9539458
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202203127
Membrane compartmentalization of Ect2/Cyk4/Mklp1 and NuMA/dynein regulates cleavage furrow formation
Abstract
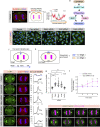
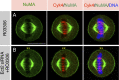
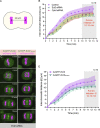
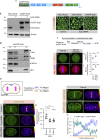
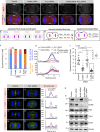
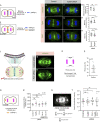
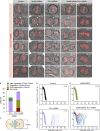
In animal cells, spindle elongation during anaphase is temporally coupled with cleavage furrow formation. Spindle elongation during anaphase is regulated by NuMA/dynein/dynactin complexes that occupy the polar region of the cell membrane and are excluded from the equatorial membrane. How NuMA/dynein/dynactin are excluded from the equatorial membrane and the biological significance of this exclusion remains unknown. Here, we show that the centralspindlin (Cyk4/Mklp1) and its interacting partner RhoGEF Ect2 are required for NuMA/dynein/dynactin exclusion from the equatorial cell membrane. The Ect2-based (Ect2/Cyk4/Mklp1) and NuMA-based (NuMA/dynein/dynactin) complexes occupy mutually exclusive membrane surfaces during anaphase. The equatorial membrane enrichment of Ect2-based complexes is essential for NuMA/dynein/dynactin exclusion and proper spindle elongation. Conversely, NuMA-based complexes at the polar region of the cell membrane ensure spatially confined localization of Ect2-based complexes and thus RhoA. Overall, our work establishes that membrane compartmentalization of NuMA-based and Ect2-based complexes at the two distinct cell surfaces restricts dynein/dynactin and RhoA for coordinating spindle elongation with cleavage furrow formation.
© 2022 Sana et al.
Figures






Similar articles
-
NuMA interacts with phosphoinositides and links the mitotic spindle with the plasma membrane.EMBO J. 2014 Aug 18;33(16):1815-30. doi: 10.15252/embj.201488147. Epub 2014 Jul 4. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 24996901 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-regulated cortical dynein/dynactin promotes symmetric cell division by differential pole motion in anaphase.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Sep;23(17):3380-90. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-02-0109. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22809624 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin B degradation leads to NuMA release from dynein/dynactin and from spindle poles.EMBO Rep. 2004 Jan;5(1):97-103. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400046. EMBO Rep. 2004. PMID: 14710193 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NuMA in vertebrate cells: review of an intriguing multifunctional protein.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:1137-46. doi: 10.2741/1868. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146802 Review.
-
Cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin in cell division and intracellular transport.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;11(1):45-53. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80006-4. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10047518 Review.
Cited by
-
The Expression Regulation and Cancer-Promoting Roles of RACGAP1.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 24;15(1):3. doi: 10.3390/biom15010003. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39858398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cortical pool of LIN-5 (NuMA) controls cytokinetic furrow formation and cytokinesis completion.J Cell Biol. 2025 Jul 7;224(7):e202406059. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202406059. Epub 2025 Apr 30. J Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40304693 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

