Analysis of the complete plastomes and nuclear ribosomal DNAs from Euonymus hamiltonianus and its relatives sheds light on their diversity and evolution
- PMID: 36197898
- PMCID: PMC9534445
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275590
Analysis of the complete plastomes and nuclear ribosomal DNAs from Euonymus hamiltonianus and its relatives sheds light on their diversity and evolution
Abstract
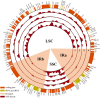
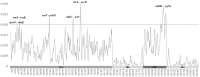
Euonymus hamiltonianus and its relatives (Celastraceae family) are used for ornamental and medicinal purposes. However, species identification in Euonymus is difficult due to their morphological diversity. Using plastid genome (plastome) data, we attempt to reveal phylogenetic relationship among Euonymus species and develop useful markers for molecular identification. We assembled the plastome and nuclear ribosomal DNA (nrDNA) sequences from five Euonymus lines collected from South Korea: three Euonymus hamiltonianus accessions, E. europaeus, and E. japonicus. We conducted an in-depth comparative analysis using ten plastomes, including other publicly available plastome data for this genus. The genome structures, gene contents, and gene orders were similar in all Euonymus plastomes in this study. Analysis of nucleotide diversity revealed six divergence hotspots in their plastomes. We identified 339 single nucleotide polymorphisms and 293 insertion or deletions among the four E. hamiltonianus plastomes, pointing to abundant diversity even within the same species. Among 77 commonly shared genes, 9 and 33 were identified as conserved genes in the genus Euonymus and E. hamiltonianus, respectively. Phylogenetic analysis based on plastome and nrDNA sequences revealed the overall consensus and relationships between plastomes and nrDNAs. Finally, we developed six barcoding markers and successfully applied them to 31 E. hamiltonianus lines collected from South Korea. Our findings provide the molecular basis for the classification and molecular taxonomic criteria for the genus Euonymus (at least in Korea), which should aid in more objective classification within this genus. Moreover, the newly developed markers will be useful for understanding the species delimitation of E. hamiltonianus and closely related species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elucidating time divergence and biogeography of Euonymus hamiltonianus complex using complete plastome analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 14;15(1):29905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13321-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40813590 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of Chiloschista (Orchidaceae) species and DNA barcoding investigation based on plastid genomes.BMC Genomics. 2023 Dec 6;24(1):749. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09847-8. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 38057701 Free PMC article.
-
Authentication of Allium ulleungense, A. microdictyon and A. ochotense based on super-barcoding of plastid genome and 45S nrDNA.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 20;18(11):e0294457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294457. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37983242 Free PMC article.
-
Cold Resistance of Euonymus japonicus Beihaidao Leaves and Its Chloroplast Genome Structure and Comparison with Celastraceae Species.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 20;11(19):2449. doi: 10.3390/plants11192449. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36235317 Free PMC article.
-
Progress, challenge and prospect of plant plastome annotation.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 30;14:1166140. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1166140. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37324662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A First Approach for the In Vitro Cultivation, Storage, and DNA Barcoding of the Endangered Endemic Species Euonymus koopmannii.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 6;13(16):2174. doi: 10.3390/plants13162174. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204610 Free PMC article.
-
A recent large-scale intraspecific IR expansion and evolutionary dynamics of the plastome of Peucedanum japonicum.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84540-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39748098 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating time divergence and biogeography of Euonymus hamiltonianus complex using complete plastome analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 14;15(1):29905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13321-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40813590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li YN, Xie L, Li JY, Zhang ZX. Phylogeny of Euonymus inferred from molecular and morphological data. J Syst Evol. 2014; 52(2): 149–160. doi: 10.1111/jse.12068 - DOI
-
- Schulz B. Studies of fruit and seed characters of selected Euonymus species.(Translated by Wolfgang Bopp). International Dendrology Society Yearbook; 2006. pp. 30–52.
-
- Li Y, Dong Y, Liu Y, Yu X, Yang M, Huang Y. Comparative analyses of Euonymus chloroplast genomes: Genetic structure, screening for loci with suitable polymorphism, positive selection genes, and phylogenetic relationships within Celastrineae. Front Plant Sci. 2020; 11: 2307. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.593984 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christenhusz MJ, Byng JW. The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa. 2016; 261(3): 201–217. doi: 10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

