Deficit in observational learning in experimental epilepsy
- PMID: 36197904
- PMCID: PMC10092486
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.17421
Deficit in observational learning in experimental epilepsy
Abstract
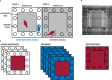
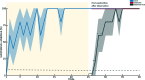
Individuals use the observation of a conspecific to learn new behaviors and skills in many species. Whether observational learning is affected in epilepsy is not known. Using the pilocarpine rat model of epilepsy, we assessed learning by observation in a spatial task. The task involves a naive animal observing a demonstrator animal seeking a reward at a specific spatial location. After five observational sessions, the observer is allowed to explore the rewarded space and look for the reward. Although control observer rats succeed in finding the reward when allowed to explore the rewarded space, epileptic animals fail. However, epileptic animals are able to successfully learn the location of the reward through their own experience after several trial sessions. Thus, epileptic animals show a clear deficit in learning by observation. This result may be clinically relevant, in particular in children who strongly rely on observational learning.
Keywords: animal model; observational learning; social behavior; spatial memory.
© 2022 The Authors. Epilepsia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Social Learning of a Spatial Task by Observation Alone.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jul 13;16:902675. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.902675. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35910679 Free PMC article.
-
Observational learning of a shifting goal location in rats: Impact of distance, observed performance, familiarity, and delay.J Neurosci Methods. 2020 Apr 1;335:108617. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108617. Epub 2020 Jan 31. J Neurosci Methods. 2020. PMID: 32014445
-
Observational learning in rats: Interplay between demonstrator and observer behavior.J Neurosci Methods. 2023 Mar 15;388:109807. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2023.109807. Epub 2023 Jan 31. J Neurosci Methods. 2023. PMID: 36731637
-
Hippocampal-dependent spatial memory in the water maze is preserved in an experimental model of temporal lobe epilepsy in rats.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022372. Epub 2011 Jul 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829459 Free PMC article.
-
Grey squirrels (Sciurus carolinensis) show a feature-negative effect specific to social learning.Anim Cogn. 2010 Mar;13(2):219-27. doi: 10.1007/s10071-009-0259-3. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Anim Cogn. 2010. PMID: 19588175
References
-
- Bandura A, Ross D, Ross SA. Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1961;63:575–82. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1986. 10.1017/S0813483900008238 - DOI
-
- Bandura A. Observational learning. In: Wolfgang D editor. The international encyclopedia of communication. Chichester, UK. John Wiley & Sons; 2008. p.1–3. 10.1002/9781405186407.wbieco004 - DOI
-
- Kostorz K, Flanagin VL, Glasauer S. Synchronization between instructor and observer when learning a complex bimanual skill. Neuroimage. 2020;216:116659. - PubMed

