Diagnostic yield and safety of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy and surgical lung biopsy in interstitial lung diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36198419
- PMCID: PMC9724793
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0280-2021
Diagnostic yield and safety of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy and surgical lung biopsy in interstitial lung diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) is increasingly being used as an alternative to video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) biopsy to establish the histopathologic pattern in interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Methods: A systematic literature search of the PubMed and Embase databases, from October 2010 to October 2020, was conducted to identify studies that reported on diagnostic yield or safety of VATS or TBLC in the diagnosis of ILD.
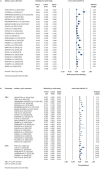
Results: 43 studies were included. 23 evaluated the diagnostic yield of TBLC after multidisciplinary discussion, with a pooled diagnostic yield of 76.8% (95% confidence interval (CI) 70.6-82.1), rising to 80.7% in centres that performed ≥70 TBLC. 10 studies assessed the use of VATS and the pooled diagnostic yield was 93.5% (95% CI 88.3-96.5). In TBLC, pooled incidences of complications were 9.9% (95% CI 6.8-14.3) for significant bleeding (6.9% for centres with ≥70 TBLC), 5.6% (95% CI 3.8-8.2) for pneumothorax treated with a chest tube and 1.4% (95% CI 0.9-2.2) for acute exacerbation of ILD after TBLC. The mortality rates were 0.6% and 1.7% for TBLC and VATS, respectively.
Conclusions: TBLC has a fairly good diagnostic yield, an acceptable safety profile and a lower mortality rate than VATS. The best results are obtained from more experienced centres.
Copyright ©The authors 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: H. Novais Bastos has received support from Sociedade Portuguesa de Pneumologia, as well as grants or contracts from Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia and Fundação Amélia de Mello/CUF; consulting fees from Boehringer-Ingelheim and Roche; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Boehringer-Ingelheim and Roche; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Boehringer-Ingelheim; and equipment, materials, drugs, medical writing, gifts or other services from Boehringer-Ingelheim, all outside the submitted work. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, et al. . An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013; 188: 733–748. doi:10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kadoch MA, Cham MD, Beasley MB, et al. . Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: a radiology-pathology correlation based on the revised 2013 American Thoracic Society-European Respiratory Society classification system. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 2015; 44: 15–25. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2014.07.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
