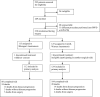
A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Clinical Trial Comparing Cattell-Warren and Blumgart Anastomoses Following Partial Pancreatoduodenectomy: PANasta Trial
- PMID: 36199490
- PMCID: PMC9508971
- DOI: 10.1097/AS9.0000000000000198
A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Clinical Trial Comparing Cattell-Warren and Blumgart Anastomoses Following Partial Pancreatoduodenectomy: PANasta Trial
Abstract
Whether a Blumgart anastomosis (BA) is superior to Cattell-Warren anastomosis (CWA) in terms of postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) following pancreatoduodenectomy.
Importance: Complications driven by POPF following pancreatic cancer resection may hinder adjuvant therapy, shortening survival. BA may reduce complications compared to CWA, improving the use of adjuvant therapy and prolonging survival.
Methods: A multicenter double-blind, controlled trial of patients undergoing resection for suspected pancreatic head cancer, randomized during surgery to a BA or CWA, stratified by pancreatic consistency and duct diameter. The primary end point was POPF, and secondary outcome measures were adjuvant therapy use, specified surgical complications, quality of life, and survival from the date of randomization. For a 10% POPF reduction, 416 patients were required, 208 per arm (two-sided α = 0·05; power = 80%).
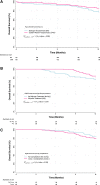
Results: Z-score at planned interim analysis was 0.474 so recruitment was held to 238 patients; 236 patients were analyzed (112 BA and 124 CWA). No significant differences in POPF were observed between BA and CWA, odds ratio (95% confidence interval [CI]) 1·04 (0.58-1.88), P = 0.887, nor in serious adverse events. Adjuvant therapy was delivered to 98 (62%) of 159 eligible patients with any malignancy; statistically unrelated to arm or postoperative complications. Twelve-month overall survival, hazard ratio (95% CI), did not differ between anastomoses; BA 0.787 (0.713-0.868) and CWA 0.854 (0.792-0.921), P = 0.266, nor for the 58 patients with complications, median (IQR), 0.83 (0.74-0.91) compared to 101 patients without complications 0.82 (0.76-0.89) (P = 0.977).
Conclusions: PANasta represents the most robust analysis of BA versus CWA to date.
Keywords: blumgart anastomosis; cattell-warren anastomosis; complications; pancreatic adenocarcinoma; pancreatico-jejunostomy; post operative pancreatic fistula; survival.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Kleeff J, Korc M, Apte M, et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16022. - PubMed
-
- [online] G. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: International Agency for Research on Cancer Available at: http://globocan.iarc.fr. Accessed January 26, 2022.
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Conroy T, Hammel P, Hebbar M, et al. ; Canadian Cancer Trials Group and the Unicancer-GI–PRODIGE Group. FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2395–2406. - PubMed
-
- Neoptolemos JP, Stocken DD, Friess H, et al. ; European Study Group for Pancreatic Cancer. A randomized trial of chemoradiotherapy and chemotherapy after resection of pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1200–1210. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources