Construction and Evaluation of a Preoperative Prediction Model for Lymph Node Metastasis of cIA Lung Adenocarcinoma Using Random Forest
- PMID: 36199801
- PMCID: PMC9527416
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4008113
Construction and Evaluation of a Preoperative Prediction Model for Lymph Node Metastasis of cIA Lung Adenocarcinoma Using Random Forest
Abstract
Background: Lymph node metastasis (LNM) is the main route of metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma (LA), and preoperative prediction of LNM in early LA is key for accurate medical treatment. We aimed to establish a preoperative prediction model of LNM of early LA through clinical data mining to reduce unnecessary lymph node dissection, reduce surgical injury, and shorten the operation time.
Methods: We retrospectively collected imaging data and clinical features of 1121 patients with early LA who underwent video-assisted thoracic surgery at the First Hospital of China Medical University from 2004 to 2021. Logistic regression analysis was used to select variables and establish the preoperative diagnosis model using random forest classifier (RFC). The prediction results from the test set were used to evaluate the prediction performance of the model.
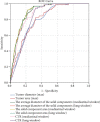
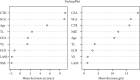
Results: Combining the results of logistic analysis and practical clinical application experience, nine clinical features were included. In the random forest classifier model, when the number of nodes was three and the n-tree value is 500, we obtained the best prediction model (accuracy = 0.9769), with a positive prediction rate of 90% and a negative prediction rate of 98.69%.
Conclusion: We established a preoperative prediction model for LNM of early LA using a machine learning random forest method combined with clinical and imaging features. More excellent predictors may be obtained by refining imaging features.
Copyright © 2022 Chuhan Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources