The effectiveness of erysipelas prophylaxis depends on the cumulative dose of benzathine penicillin G
- PMID: 36199905
- PMCID: PMC9527694
- DOI: 10.4081/dr.2022.9429
The effectiveness of erysipelas prophylaxis depends on the cumulative dose of benzathine penicillin G
Abstract
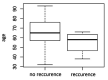
Erysipelas is an acute infection due to S. pyogenes and is characterized by a high risk of relapses. The number of patients suffering from one or more recurrences varied depending on the study and accounted for between 16% and 47% of the total number of those affected. Antibiotic prophylaxis with the use of penicillin can reduce the risk of recurrence by 47%. A number of 873 patients with erysipelas treated at the Hospital for Infectious Diseases in Warsaw from 2010 to 2018 was enrolled in the study. Benzathine-penicillin G was given intramuscularly at a dose of 1.2 MU or 2.4 MU or 3.6 MU. The earliest moment that prophylactic treatment was administered was the first episode of erysipelas recurrence. The decision to administer the antibiotic and the dose to use was discretionally made by the examining physician. Altogether 104 (11.9%) persons experienced at least one episode of erysipelas recurrence during the study period. A total of 2976 doses of benzathine- penicillin G (BP) were administered. The most common dose was that of 2.4 MU (2380, 80%). The dose of 1.2 MU was given 567 times (19%). The highest dose, i.e. 3.6 MU, was administered to only 5 patients (8 applications, 0.2%). No effect was shown by either the number of benzathine- penicillin G administered doses (p=0.07) or the median dose (p=0.65), whereas patients without relapse received a statistically higher cumulative dose of the antibiotic (p=0.047). Age was a risk factor of recurrence only in the group of diabetic patients (p=0.03). Benzathine penicillin G given in an appropriate cumulative dose is effective in preventing erysipelas recurrence.
Keywords: Benzathine penicillin G; Cumulative dose; Erysipelas; Recurrence.
©Copyright: the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Benzathine penicillin G once-every-3-week prophylaxis for recurrent erysipelas a retrospective study of 132 patients.J Dermatolog Treat. 2018 Feb;29(1):39-43. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2017.1329507. Epub 2017 May 30. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018. PMID: 28489486
-
Recurrence of lymphoedema-associated cellulitis (erysipelas) under prophylactic antibiotherapy: a retrospective cohort study.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006 Aug;20(7):818-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2006.01648.x. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006. PMID: 16898904
-
Rheumatic fever prophylaxis in South Africa--is bicillin 1,2 million units every 4 weeks appropriate?S Afr Med J. 1994 Aug;84(8 Pt 1):477-81. S Afr Med J. 1994. PMID: 7825080
-
[Therapy and prophylaxis of recurrent erysipelas (author's transl)].Med Klin. 1976 Jul 9;71:1197-9. Med Klin. 1976. PMID: 822266 German.
-
[Infectious complications of lymphedema].Rev Med Interne. 2002 Jun;23 Suppl 3:403s-407s. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(02)80383-6. Rev Med Interne. 2002. PMID: 12162204 Review. French.
References
-
- Chlebicki MP, Oh CC. Recurrent Cellulitis: Risk, Factors, Etiology, Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2014;16:422. - PubMed
-
- Kasper DL, Fauci AS. Harrison's Infectious Diseases. 3rd ed. McGraw- Hill Education; 2017.
-
- Leclerc S, Teixeira A, Mahe E, et al. . Recurrent Erysipelas: 47 Cases. Dermatology 2007;2014:52-7. - PubMed
-
- Rob F, Hercegova J. Benzathine penicillin G once-every-3-week prophylaxis for recurrent erysipelas: a retrospective study of 132 patients. J Dermatolog Treat 2018;29:39-4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials