Reciprocal signaling between adipose tissue depots and the central nervous system
- PMID: 36200038
- PMCID: PMC9529070
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.979251
Reciprocal signaling between adipose tissue depots and the central nervous system
Abstract
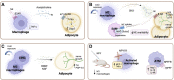
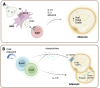
In humans, various dietary and social factors led to the development of increased brain sizes alongside large adipose tissue stores. Complex reciprocal signaling mechanisms allow for a fine-tuned interaction between the two organs to regulate energy homeostasis of the organism. As an endocrine organ, adipose tissue secretes various hormones, cytokines, and metabolites that signal energy availability to the central nervous system (CNS). Vice versa, the CNS is a critical regulator of adipose tissue function through neural networks that integrate information from the periphery and regulate sympathetic nerve outflow. This review discusses the various reciprocal signaling mechanisms in the CNS and adipose tissue to maintain organismal energy homeostasis. We are focusing on the integration of afferent signals from the periphery in neuronal populations of the mediobasal hypothalamus as well as the efferent signals from the CNS to adipose tissue and its implications for adipose tissue function. Furthermore, we are discussing central mechanisms that fine-tune the immune system in adipose tissue depots and contribute to organ homeostasis. Elucidating this complex signaling network that integrates peripheral signals to generate physiological outputs to maintain the optimal energy balance of the organism is crucial for understanding the pathophysiology of obesity and metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: adipogenesis; adipose tissue; adipose tissue macrophage; central nervous system; hypothalamus; lipolysis; resident immune cells; sympathetic regulation.
Copyright © 2022 Puente-Ruiz and Jais.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor SU declared a shared affiliation with the authors at the time of review.
Figures

References
-
- Barbe P., Millet L., Galitzky J., Lafontan M., Berlan M. (1996). In situ assessment of the role of the beta 1-beta 2- and beta 3-adrenoceptors in the control of lipolysis and nutritive blood flow in human subcutaneous adipose tissue. Br. J. Pharmacol. 117, 907–913. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15279.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

