Estradiol and zinc-doped nano hydroxyapatite as therapeutic agents in the prevention of osteoporosis; oxidative stress status, inflammation, bone turnover, bone mineral density, and histological alterations in ovariectomized rats
- PMID: 36200054
- PMCID: PMC9527315
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.989487
Estradiol and zinc-doped nano hydroxyapatite as therapeutic agents in the prevention of osteoporosis; oxidative stress status, inflammation, bone turnover, bone mineral density, and histological alterations in ovariectomized rats
Abstract
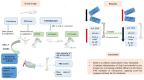
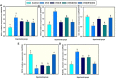
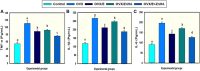
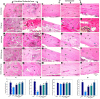
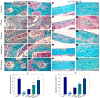
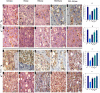
Osteoporosis (OP) is a serious health problem, and the most popular therapeutic strategy for OP is hormone replacement (estrogen); however, it increases the risk of reproductive cancers. Hydroxyapatite (HA) nanoparticles have a similar chemical structure to the bone mineral component and can be used as a new remedy for OP. This study was designed to investigate the osteoporosis-protective potential of nano zinc hydroxyapatite (ZnHA-NPs) and/or estradiol (E2) combined therapy. A total of 35 adult female rats were assigned into five groups (n = 7): 1) control group; 2) ovariectomized group (OVX); 3) OVX received oral estradiol replacement therapy (OVX/E2); 4) OVX received ZnHA replacement therapy (OVX/ZnHA); and 5) OVX received both estradiol and ZnHA-NPs combined therapy (OVX/E2+ZnHA). After 3 months of treatment, serum bone markers and estrogen level, oxidative/antioxidant, and inflammatory cytokines were determined. Additionally, femoral expression of estrogen receptors alpha and beta (ESR1; ESR2), receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B (RANKL) ligand, osteoprotegerin (OPG), bone mineral density (BMD), histological alterations, and immunohistochemical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) were assessed. ALP, PINP, Ca, and P concentrations improved significantly (p < 0.05) in all treatment groups, especially in the OVX/E + ZnHA group. MDA and NO were higher in OVX rats, while SOD activity and GSH were lower (p < 0.05). E2 alone or with ZnHA-NPs restored the estimated antioxidant molecules and cytokines toward normal levels in OVX rats (p < 0.05). On the other hand, E2 and ZnHA increased OPG and OC expression in femurs while decreasing ESR1, ESR2, and NF-kB expression (p < 0.05). The combination treatment was superior in the restoration of normal femoral histoarchitecture and both cortical and trabecular BMD (p < 0.05). Overall, the combined therapy of OVX/E2+ZnHA was more effective than the individual treatments in attenuating excessive bone turnover and preventing osteoporosis.
Keywords: Osteoporosis; PINP/VEGF/PCNA; estradiol; oxidative/inflammatory markers; zinc-doped nano hydroxyapatite.
Copyright © 2022 Elghareeb, Elshopakey, Elkhooly, Salama, Samy, Bazer, Elmetwally, Almutairi, Aleya, Abdel-Daim and Rezk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abdel-Fattah W. I., Reicha F. M., Elkhooly T. A. (2008). Characterization of nano-biphasic calcium phosphates synthesized under microwave curing. JNanoR. 3, 67–87. 10.4028/www.scientific.net/jnanor.3.67 - DOI
-
- Albertazzi P., Steel S., Howarth E., Purdie D. (2004). Comparison of the effects of two different types of calcium supplementation on markers of bone metabolism in a postmenopausal osteopenic population with low calcium intake: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Climacteric 7, 33–40. 10.1080/13697130310001651454 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

