Characterization of PsmiR319 during flower development in early- and late-flowering tree peonies cultivars
- PMID: 36200538
- PMCID: PMC9542857
- DOI: 10.1080/15592324.2022.2120303
Characterization of PsmiR319 during flower development in early- and late-flowering tree peonies cultivars
Abstract
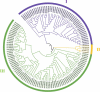
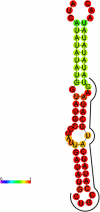
The flowering period is the most important ornamental trait of tree peony, while industrial development of tree peony has been limited by short flowering period. miR319 plays an important regulatory role in plant flowering. In the current study, the expression characteristics and evolution of PsmiR319 in tree peony flowering was explored using 'Feng Dan' and 'Lian He', which are early-flowering and late-flowering varieties of tree peony, respectively. The structure, evolution, and target(s) of PsmiR319 were analyzed by bioinformatics. Evolution analysis showed that pre-PsmiR319 was distributed in 41 plant species, among which the length of the precursor sequence exhibited marked differences (between 52 and 308 bp). Pre-PsmiR319 of tree peony was located close to the corresponding sequences of Linum usitatissimum and Picea abies in the phylogenetic tree, and in addition, could form a typical hairpin structure including a mature body with a length of 20 bp located on the 3p arm and part of the loop sequence. The mature sequence of miR319 was highly conserved among different species. Target genes of PsmiR319 include MYB-related transcription factor in tree peony. Expression of PsmiR319, assayed by qRT-PCR, differed between 'Feng Dan' and 'Lian He' during different flower development periods. PsmiR319 and its target gene showed a negative expression regulation relationship during the periods of CE (color exposure), BS (blooming stage), IF (initial flowering), and HO (half opening) in the early-flowering 'Feng Dan', and the same in FB (Full blooming) periods of late-flowering 'Lian He'. Findings from this study provide a reference for further investigation into the mechanism of miR319 in the development of different varieties of tree peony.
Keywords: PsmiR319; Tree peony; early and late flowering; expression analysis; flower development.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Screening of Genes Related to Early and Late Flowering in Tree Peony Based on Bulked Segregant RNA Sequencing and Verification by Quantitative Real-Time PCR.Molecules. 2018 Mar 19;23(3):689. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030689. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29562683 Free PMC article.
-
De novo sequencing of tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa) transcriptome to identify critical genes involved in flowering and floral organ development.BMC Genomics. 2019 Jul 11;20(1):572. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5857-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31296170 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs and their target genes in response to brassinolide treatment on flowering of tree peony (Paeonia ostii).Plant Signal Behav. 2022 Dec 31;17(1):2056364. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2022.2056364. Plant Signal Behav. 2022. PMID: 35343364 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of PoVIN3, a Key Gene of Vernalization Pathway, Affects Flowering Time.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 13;23(22):14003. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214003. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430482 Free PMC article.
-
Flower morphology, flower color, flowering and floral fragrance in Paeonia L.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Nov 21;15:1467596. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1467596. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39640998 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the molecular secrets of Paeonia plants: advances in key gene mining and molecular breeding technology.Hortic Res. 2025 Apr 30;12(7):uhaf090. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhaf090. eCollection 2025 Jul. Hortic Res. 2025. PMID: 40352288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang L, Guo DL, Guo LL, Guo Q, Wang HF, Hou XG.. Construction of a high-density genetic map and QTLs mapping with GBS from the interspecific F1 population of P. ostii ‘Fengdan Bai’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Xin Riyuejin’. Sci Hortic. 2019;246:190–10. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.039. - DOI
-
- Wang XJ, Liang HY, Guo DL, Guo LL, Duan XG, Jia QS, Hou XG. Integrated analysis of transcriptomic and proteomic data from tree peony (P. ostii) seeds reveals key developmental stages and candidate genes related to oil biosynthesis and fatty acid metabolism. Hortic. Res. 2019;6:111. doi:10.1038/s41438-019-0194-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xue YQ, Liu R, Xue JQ, Wang SL, Zhang XX. Genetic diversity and relatedness analysis of nine wild species of tree peony based on simple sequence repeats markers. Hortic Plant J. 2021;7(6):579–588. doi:10.1016/j.hpj.2021.05.004. - DOI
-
- Zhou L, Wang Y, Peng Z. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of chalcone synthase gene during flower development in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa). Afr J Biotechnol. 2011;10(8):1275–1284. doi:10.5897/AJB10.599. - DOI
-
- Xi HV, He YJ, Chen HY. Functional characterization of SmbHLH13 in anthocyanin biosynthesis and flowering in eggplant. Hortic Plant J. 2021;7(1):73–80. doi:10.1016/j.hpj.2020.08.006. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
