Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphism is associated with chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer who receive chemotherapy
- PMID: 36200595
- PMCID: PMC10028021
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5319
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphism is associated with chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer who receive chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (CRCI) is a common but easily overlooked condition that markedly affects the quality of life (QOL) of patients with breast cancer. The rs671 is a common gene polymorphism of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) in Asia that is involved in aldehyde metabolism and may be closely related to CRCI. However, no study has yet summarised the association between ALDH2 and CRCI.
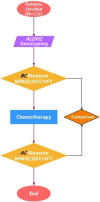
Methods: This study enrolled one hundred and twenty-four patients diagnosed with breast cancer according to the pathology results, genotyped for ALDH2 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) to explore these. The mini-mental state exam (MMSE), verbal fluency test (VFT), and digit span test (DST) results were compared in these patients before and after chemotherapy (CT).
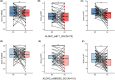
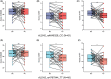
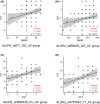
Results: We found that patients with ALDH2 gene genotypes of rs671_GG, rs886205_GG, rs4648328_CC, and rs4767944_TT polymorphisms were more likely to suffer from cognitive impairment during chemotherapy. A trend toward statistical significance was observed for rs671_GG of DST (z = 2.769, p = 0.006), VFT (t = 4.624, P<0.001); rs886205_GG of DST (z = 3.663, P<0.001); rs4648328_CC of DST (z = 2.850, p = 0.004), VFT (t = 3.477, p = 0.001); and rs4767944_TT of DST (z = 2.967, p = 0.003), VFT (t = 2.776, p = 0.008). The cognitive indicators of these patients significantly decreased after chemotherapy (p < 0.05). The difference in ALDH2 rs671 was most obvious.
Conclusion: Our results showed what kinds of ALDH2 genotyped patients that are more likely to develop CRCI. In the future, it may be possible to infer the risk of CRCI by detecting the single-nucleotide locus of ALDH2 that is conducive to strengthening clinical interventions for these patients and improving their QOL. More importantly, this study has important implications for Asian women with breast cancer as ALDH2 rs671 is a common polymorphism in Asians.
Keywords: CRCI; breast cancer survivors; chemotherapy; cognitive impairment.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase Polymorphism with Spontaneous Deep Intracerebral Haemorrhage in the Taiwan population.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 27;10(1):3641. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60567-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32107439 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 rs671 Polymorphism Affects Hypertension Susceptibility and Lipid Profiles in a Chinese Population.DNA Cell Biol. 2019 Sep;38(9):962-968. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.4647. Epub 2019 Jul 30. DNA Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31361523
-
Effect of ALDH2 on Sleep Disturbances in Patients with Parkinson's Disease.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 12;9(1):18950. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55427-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31831791 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between the Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 rs671 G>A Polymorphism and Head and Neck Cancer Susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis in East Asians.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Feb;45(2):307-317. doi: 10.1111/acer.14527. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 33283290
-
Advances of neuroimaging in chemotherapy related cognitive impairment (CRCI) of patients with breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Aug;201(1):15-26. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07005-y. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37329458 Review.
References
-
- Chen J, Haanpää MK, Gruber JJ, Jäger N, Ford JM, Snyder MP. High‐resolution bisulfite‐sequencing of peripheral blood DNA methylation in early‐onset and familial risk breast cancer patients. Clinical Cancer Research: An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2019;25(17):5301–14. Epub 2019/06/09. PubMed PMID: 31175093; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC6726519. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-18-2423 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N, Chen WQ. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(7):783–91. Epub 2021/03/19. PubMed PMID: 33734139; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC8104205. doi:10.1097/cm9.0000000000001474 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

