Thais savignyi tissue extract: bioactivity, chemical composition, and molecular docking
- PMID: 36200747
- PMCID: PMC9553184
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2123940
Thais savignyi tissue extract: bioactivity, chemical composition, and molecular docking
Abstract
Context: Thais savignyi Deshayes (Muricidae) is widely distributed in the Red Sea. Its abundance and the history of Muricidae in traditional medicine make it a tempting target for investigation.
Objective: To investigate the chemical profile and biological activities of T. savignyi tissue extracts.
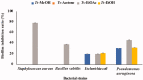
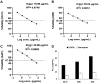
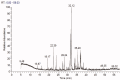
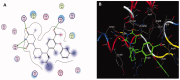
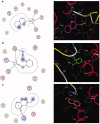
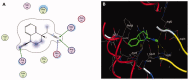
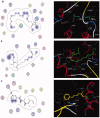
Materials and methods: Methanol, ethanol, acetone, and ethyl acetate extracts from T. savignyi tissue were compared in their antioxidant by total antioxidant capacity, DPPH free radical scavenging, and total phenolic content. In addition, the antimicrobial, and antibiofilm properties (at 250 µg/mL) of the extracts were tested against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus vulgaris, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans. The antioxidant extract with greatest activity was assessed for cytotoxicity (range 0.4-100 µg/mL) against 3 human cancer cell lines (UO-31, A549 and A431), and its chemical composition was investigated using GC-MS. Moreover, docking simulation was performed to predict its constituents' binding modes/scores to the active sites of thymidylate kinase.
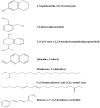
Results: The ethyl acetate extract (Ts-EtOAc) showed the highest total antioxidant capacity (551.33 mg AAE/g dry weight), total phenolics (254.46 mg GAE/g dry weight), and DPPH scavenging (IC50= 24.0 µg/mL). Ts-EtOAc exhibited strong antibacterial (MIC: 3.9 µg/mL against K. pneumoniae), antibiofilm (MIC: 7.81 µg/mL against S. aureus), and antifungal (MIC: 3.9 µg/mL against C. albicans) activities and considerable cytotoxicity against cancer cells (UO-31: IC50= 19.96 ± 0.93, A549: IC50= 25.04 ± 1.15 μg/mL). GC-MS identified multiple bioactive metabolites in Ts-EtOAc extract belonging to miscellaneous chemical classes. Molecular docking studies revealed that the constituents of Ts-EtOAc have antibacterial potential.
Discussion and conclusions: T. savignyi extract has considerable antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities. Further studies are needed to isolate the active constituents of this snail for comprehensive drug discovery tests.
Keywords: Antioxidant; antimicrobial; bioactive compounds; cytotoxicity; marine snails.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Abdel-Aziz MS, Ghareeb MA, Saad AM, Refahy LA, Hamed AA.. 2018. Chromatographic isolation and structural elucidation of secondary metabolites from the soil-inhabiting fungus Aspergillus fumigatus 3T-EGY. Acta Chromatogr. 30(4):243–249.
-
- Abu El-Einin AA, Gad El-Karim RM, Habib MR, Zayed KM, Ali REM.. 2021. Identification of the gastropod snails and shells collected from Ain El-Sokhna region, Red Sea, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Biol Fisher. 25:101–117.
-
- Adams RP. 2007. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (vol. 456). Carol Stream (IL): Allured Publishing Corporation.
-
- Ahmad TB, Liu L, Kotiw M, Benkendorff K.. 2018. Review of anti-inflammatory, immune-modulatory and wound healing properties of molluscs. J Ethnopharmacol. 210:156–178. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
