APE1 assembles biomolecular condensates to promote the ATR-Chk1 DNA damage response in nucleolus
- PMID: 36200829
- PMCID: PMC9561277
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac853
APE1 assembles biomolecular condensates to promote the ATR-Chk1 DNA damage response in nucleolus
Abstract
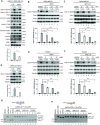
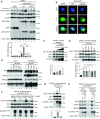
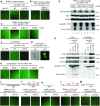
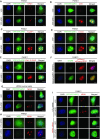
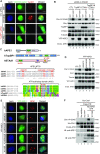
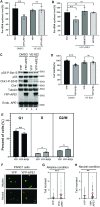
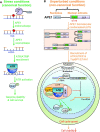
Multifunctional protein APE1/APEX1/HAP1/Ref-1 (designated as APE1) plays important roles in nuclease-mediated DNA repair and redox regulation in transcription. However, it is unclear how APE1 regulates the DNA damage response (DDR) pathways. Here we show that siRNA-mediated APE1-knockdown or APE1 inhibitor treatment attenuates the ATR-Chk1 DDR under stress conditions in multiple immortalized cell lines. Congruently, APE1 overexpression (APE1-OE) activates the ATR DDR under unperturbed conditions, which is independent of APE1 nuclease and redox functions. Structural and functional analysis reveals a direct requirement of the extreme N-terminal motif within APE1 in the assembly of distinct biomolecular condensates in vitro and DNA/RNA-independent activation of the ATR DDR. Overexpressed APE1 co-localizes with nucleolar NPM1 and assembles biomolecular condensates in nucleoli in cancer but not non-malignant cells, which recruits ATR and activator molecules TopBP1 and ETAA1. APE1 protein can directly activate ATR to phosphorylate its substrate Chk1 in in vitro kinase assays. W119R mutant of APE1 is deficient in nucleolar condensation, and is incapable of activating nucleolar ATR DDR in cells and ATR kinase in vitro. APE1-OE-induced nucleolar ATR DDR activation leads to compromised ribosomal RNA transcription and reduced cell viability. Taken together, we propose distinct mechanisms by which APE1 regulates ATR DDR pathways.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

