Revisiting idiopathic eosinophilic myositis: towards a clinical-pathological continuum from the muscle to the fascia and skin
- PMID: 36200845
- PMCID: PMC10234208
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac556
Revisiting idiopathic eosinophilic myositis: towards a clinical-pathological continuum from the muscle to the fascia and skin
Abstract
Objectives: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies are mainly defined by inflammatory infiltrates within the muscle (lymphocytes and macrophages). Eosinophil muscle infiltration has been described in idiopathic eosinophilic myositis (IEM) and rarely in EF. This study aimed to further delineate the nosological frame of idiopathic eosinophil muscle infiltration through the exhaustive analysis of IEM and EF patients.
Methods: This multicentre retrospective case series included IEM patients diagnosed between 2000 and 2022. IEM inclusion criteria were eosinophilic muscle infiltration with myositis pathological features, after the exclusion of differential diagnoses. An additional group of EF patients diagnosed between 2016 and 2022 was constituted. Inclusion criteria were an EF diagnosis and fascia thickening with inflammatory infiltrate.
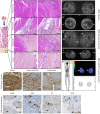
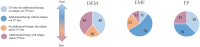
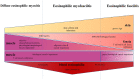
Results: A total of 20 IEM cases and 10 EF cases were included. The median (interquartile range) age at diagnosis was 65 (49-70) years; there were 18 males. Data analysis delineated four subgroups: focal EM (FEM, n = 3), diffuse EM (DEM, n = 6), eosinophilic myofasciitis (EMF, n = 11) and EF (n = 10). FEM represented a limited and benign form of myositis. DEM cases presented objective muscle impairment with eosinophilic muscle infiltration. EMF patients presented subjective muscle impairment (myalgia, 55%), fasciitis (on histology and/or imaging), eosinophilic muscle infiltration and frequent hypereosinophilia (55%). EF patients presented myalgia (50%), muscle lesions on histology with fascia-restricted inflammatory infiltrates with (60%) or without (40%) eosinophils.
Conclusions: The analysis of IEM and EF patient characteristics delineates four subgroups (FEM, DEM, EMF and EF) in terms of clinical, laboratory, imaging, pathological and outcome specificities, and proposes an adapted diagnostic and care management approach.
Keywords: Shulman syndrome; blood eosinophilia; eosinophils; idiopathic inflammatory myositis; muscle biopsy; myositis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Layzer RB, Shearn MA, Satya-Murti S.. Eosinophilic polymyositis. Ann Neurol 1977;1:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Selva-O’Callaghan A, Trallero-Araguás E, Grau JM.. Eosinophilic myositis: an updated review. Autoimmun Rev 2014;13:375–8. - PubMed
-
- Fermon C, Authier FJ, Gallay L.. Idiopathic eosinophilic myositis: a systematic literature review. Neuromuscul Disord 2022;32:116–24. - PubMed
-
- Cantarini L, Volpi N, Carbotti P. et al. Eosinophilia-associated muscle disorders: an immunohistological study with tissue localisation of major basic protein in distinct clinicopathological forms. J Clin Pathol 2009;62:442–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

