Agent-based modeling predicts RAC1 is critical for ovarian cancer metastasis
- PMID: 36200848
- PMCID: PMC9727804
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E21-11-0540
Agent-based modeling predicts RAC1 is critical for ovarian cancer metastasis
Abstract
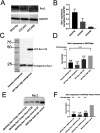
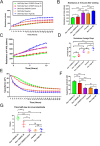
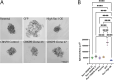
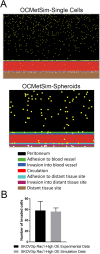
Experimental and computational studies pinpoint rate-limiting step(s) in metastasis governed by Rac1. Using ovarian cancer cell and animal models, Rac1 expression was manipulated, and quantitative measurements of cell-cell and cell-substrate adhesion, cell invasion, mesothelial clearance, and peritoneal tumor growth discriminated the tumor behaviors most highly influenced by Rac1. The experimental data were used to parameterize an agent-based computational model simulating peritoneal niche colonization, intravasation, and hematogenous metastasis to distant organs. Increased ovarian cancer cell survival afforded by the more rapid adhesion and intravasation upon Rac1 overexpression is predicted to increase the numbers of and the rates at which tumor cells are disseminated to distant sites. Surprisingly, crowding of cancer cells along the blood vessel was found to decrease the numbers of cells reaching a distant niche irrespective of Rac1 overexpression or knockdown, suggesting that sites for tumor cell intravasation are rate limiting and become accessible if cells intravasate rapidly or are displaced due to diminished viability. Modeling predictions were confirmed through animal studies of Rac1-dependent metastasis to the lung. Collectively, the experimental and modeling approaches identify cell adhesion, rapid intravasation, and survival in the blood as parameters in the ovarian metastatic cascade that are most critically dependent on Rac1.
Figures







Similar articles
-
R-Ketorolac Targets Cdc42 and Rac1 and Alters Ovarian Cancer Cell Behaviors Critical for Invasion and Metastasis.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Oct;14(10):2215-27. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0419. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26206334 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct mTORC2-dependent pathways converge on Rac1 to drive breast cancer metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 30;19(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0868-8. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28666462 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 targeting suppresses human non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma cancer stem cell activity.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 9;6(2):e16951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016951. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21347385 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine Jianpi Bushen therapy suppresses the onset of pre-metastatic niche in a murine model of spontaneous lung metastasis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Feb;86:434-440. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.013. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28012398
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
Cited by
-
Illuminating the druggable genome: Pathways to progress.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Mar;29(3):103805. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103805. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 37890715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simulation approach for common female cancers: a brief review.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 9;15:1479225. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1479225. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40703544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Applied BioPhysics (2021). Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS), https://www.biophysics.com/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

