Apelin as a new therapeutic target for COVID-19 treatment
- PMID: 36200913
- PMCID: PMC9619586
- DOI: 10.1093/qjmed/hcac229
Apelin as a new therapeutic target for COVID-19 treatment
Abstract
Background: Apelin is an endogenous neuropeptide that binds to the G-protein-coupled receptor (APJ) and participates in a variety of physiological processes in the heart, lungs and other peripheral organs. Intriguingly, [Pyr1]-Apelin-13, a highly potent pyroglutamic form of apelin, has the potential to bind to and be degraded by angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ACE2 is known to operate as a viral receptor in the early stages of severe acute respiratory coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection.
Aim: This study aimed to determine if apelin protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection by inhibiting ACE2 binding to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
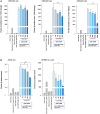
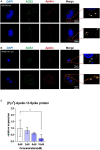
Design and methods: To determine whether [Pyr1]-Apelin-13 inhibits ACE2 binding to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (S protein), we performed a cell-to-cell fusion assay using ACE2-expressing cells and S protein-expressing cells and a pseudovirus-based inhibition assay. We then analyzed publicly available transcriptome data while focusing on the beneficial effects of apelin on the lungs.
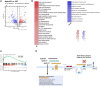
Results: We found that [Pyr1]-Apelin-13 inhibits cell-to-cell fusion mediated by ACE2 binding to the S protein. In this experiment, [Pyr1]-Apelin-13 protected human bronchial epithelial cells, infected with pseudo-typed lentivirus-producing S protein, against viral infection. In the presence of [Pyr1]-Apelin-13, the level of viral spike protein expression was also reduced in a concentration-dependent manner. Transcriptome analysis revealed that apelin may control inflammatory responses to viral infection by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa B pathway.
Conclusion: Apelin is a potential therapeutic candidate against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Association of Physicians.
Figures

References
-
- Maguire JJ, Kleinz MJ, Pitkin SL, Davenport APJH.. [Pyr1] apelin-13 identified as the predominant apelin isoform in the human heart: vasoactive mechanisms and inotropic action in disease. Hypertension 2009; 54:598–604. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

