Dicoogle Open Source: The Establishment of a New Paradigm in Medical Imaging
- PMID: 36201058
- PMCID: PMC9535235
- DOI: 10.1007/s10916-022-01867-3
Dicoogle Open Source: The Establishment of a New Paradigm in Medical Imaging
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Dicoogle Open Source: The Establishment of a New Paradigm in Medical Imaging.J Med Syst. 2022 Nov 5;46(12):92. doi: 10.1007/s10916-022-01882-4. J Med Syst. 2022. PMID: 36333520 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
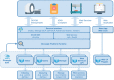
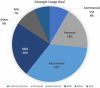
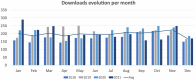
The rapid and continuous growth of data volume and its heterogeneity has become one of the most noticeable trends in healthcare, namely in medical imaging. This evolution led to the deployment of specialized information systems supported by the DICOM standard that enables the interoperability of distinct components, including imaging modalities, repositories, and visualization workstations. However, the complexity of these ecosystems leads to challenging learning curves and makes it time-consuming to mock and apply new ideas. Dicoogle is an extensible medical imaging archive server that emerges as a tool to overcome those challenges. Its extensible architecture allows the fast development of new advanced features or extends existent ones. It is currently a fundamental enabling technology in collaborative and telehealthcare environments, including research projects, screening programs, and teleradiology services. The framework is supported by a Learning Pack that includes a description of the web programmatic interface, a software development kit, documentation, and implementation samples. This article gives an in-depth view of the Dicoogle ecosystem, state-of-the-art contributions, and community impact. It starts by presenting an overview of its architectural concept, highlights some of the most representative research backed up by Dicoogle, some remarks obtained from its use in teaching, and worldwide usage statistics of the software. Finally, the positioning of Dicoogle in the medical imaging software field is discussed through comparison with other well-known solutions.
Keywords: DICOM; Dicoogle; Medical imaging; PACS; Teaching; Telehealth-care.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- K. J. Dreyer, J. H. Thrall, D. S. Hirschorn, A. Mehta (Eds.), PACS,865 Springer-Verlag, New York, 2006. 10.1007/0-387-31070-3.
-
- H.K. Huang, PACS and imaging informatics: basic principles and applications (John Wiley & Sons, 2011)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

