Incidence of Monkeypox Among Unvaccinated Persons Compared with Persons Receiving ≥1 JYNNEOS Vaccine Dose - 32 U.S. Jurisdictions, July 31-September 3, 2022
- PMID: 36201401
- PMCID: PMC9541026
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7140e3
Incidence of Monkeypox Among Unvaccinated Persons Compared with Persons Receiving ≥1 JYNNEOS Vaccine Dose - 32 U.S. Jurisdictions, July 31-September 3, 2022
Abstract
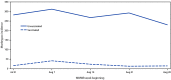
Human monkeypox is caused by Monkeypox virus (MPXV), an Orthopoxvirus, previously rare in the United States (1). The first U.S. case of monkeypox during the current outbreak was identified on May 17, 2022 (2). As of September 28, 2022, a total of 25,341 monkeypox cases have been reported in the United States.* The outbreak has disproportionately affected gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men (MSM) (3). JYNNEOS vaccine (Modified Vaccinia Ankara vaccine, Bavarian Nordic), administered subcutaneously as a 2-dose (0.5 mL per dose) series with doses administered 4 weeks apart, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2019 to prevent smallpox and monkeypox infection (4). U.S. distribution of JYNNEOS vaccine as postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) for persons with known exposures to MPXV began in May 2022. A U.S. national vaccination strategy† for expanded PEP, announced on June 28, 2022, recommended subcutaneous vaccination of persons with known or presumed exposure to MPXV, broadening vaccination eligibility. FDA emergency use authorization (EUA) of intradermal administration of 0.1 mL of JYNNEOS on August 9, 2022, increased vaccine supply (5). As of September 28, 2022, most vaccine has been administered as PEP or expanded PEP. Because of the limited amount of time that has elapsed since administration of initial vaccine doses, as of September 28, 2022, relatively few persons in the current outbreak have completed the recommended 2-dose series.§ To examine the incidence of monkeypox among persons who were unvaccinated and those who had received ≥1 JYNNEOS vaccine dose, 5,402 reported monkeypox cases occurring among males¶ aged 18-49 years during July 31-September 3, 2022, were analyzed by vaccination status across 32 U.S. jurisdictions.** Average monkeypox incidence (cases per 100,000) among unvaccinated persons was 14.3 (95% CI = 5.0-41.0) times that among persons who received 1 dose of JYNNEOS vaccine ≥14 days earlier. Monitoring monkeypox incidence by vaccination status in timely surveillance data might provide early indications of vaccine-related protection that can be confirmed through other well-controlled vaccine effectiveness studies. This early finding suggests that a single dose of JYNNEOS vaccine provides some protection against monkeypox infection. The degree and durability of such protection is unknown, and it is recommended that people who are eligible for monkeypox vaccination receive the complete 2-dose series.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Food and Drug Administration. JYNNEOS [package insert, revised June 2021]. Silver Spring, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration; 2021. https://www.fda.gov/media/131078/download
-
- Food and Drug Administration. Emergency use authorization for the emergency use of JYNNEOS. Silver Spring, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration; 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/160774/download
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

