Peripapillary atrophy classification using CNN deep learning for glaucoma screening
- PMID: 36201448
- PMCID: PMC9536646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275446
Peripapillary atrophy classification using CNN deep learning for glaucoma screening
Abstract
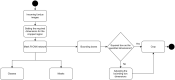
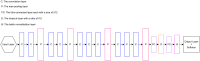
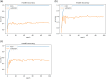
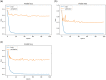
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide, and peripapillary atrophy (PPA) is a morphological symptom associated with it. Therefore, it is necessary to clinically detect PPA for glaucoma diagnosis. This study was aimed at developing a detection method for PPA using fundus images with deep learning algorithms to be used by ophthalmologists or optometrists for screening purposes. The model was developed based on localization for the region of interest (ROI) using a mask region-based convolutional neural networks R-CNN and a classification network for the presence of PPA using CNN deep learning algorithms. A total of 2,472 images, obtained from five public sources and one Saudi-based resource (King Abdullah International Medical Research Center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia), were used to train and test the model. First the images from public sources were analyzed, followed by those from local sources, and finally, images from both sources were analyzed together. In testing the classification model, the area under the curve's (AUC) scores of 0.83, 0.89, and 0.87 were obtained for the local, public, and combined sets, respectively. The developed model will assist in diagnosing glaucoma in screening programs; however, more research is needed on segmenting the PPA boundaries for more detailed PPA detection, which can be combined with optic disc and cup boundaries to calculate the cup-to-disc ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures









References
-
- Who.int. Vision impairment and blindness. 2021 Oct 14 [cited 18 Feb 2022]. In: World Health Organization [Internet]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-im....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

