Efficacy and acceptability of blue-wavelength light therapy for post-TBI behavioral symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36201498
- PMCID: PMC9536631
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274025
Efficacy and acceptability of blue-wavelength light therapy for post-TBI behavioral symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: Behavioral symptoms are common after traumatic brain injury (TBI), but their treatments remain unsatisfactory. This systematic review and meta-analysis compared the efficacy and acceptability between blue-wavelength light therapy (BWLT) and long-wavelength/no light therapy (LW/NLT) for post-TBI sleepiness, sleep disturbance, depressive symptoms, and fatigue.
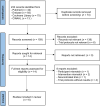
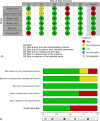
Methods: This study included randomized controlled trials comparing the effects of BWLT and LW/NLT on post-TBI sleepiness, sleep disturbance, depression, or fatigue. We searched Pubmed, Embase, CINAHL, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled of Trials on April 13, 2022. The revised tool for assessing the risk of bias in randomized trials was applied. We performed a frequentist pairwise meta-analysis using a random-effects model.
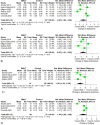
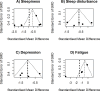
Results: Of 233 retrieved records, six trials (N = 278) were included in this meta-analysis. TBIs ranged from mild to severe, and the interventions were administered for a median of 35 days. Most trials delivered light therapy via lightboxes. Three trials had a high risk of bias. BWLT was significantly superior to LW/NLT in reducing sleep disturbance (5 trials; SMD = -0.63; 95% CI = -1.21 to -0.05; p = 0.03; I2 = 61%) and depressive symptoms (4 trials; SMD = -1.00; 95% CI = -1.62 to -0.38; p < 0.01; I2 = 56%). There were trends that BWLT was superior to LW/NLT in reducing sleepiness (6 trials; SMD = -0.92; 95% CI = -1.84 to 0.00; p = 0.05; I2 = 88%) and fatigue (4 trials; SMD = -1.44; 95% CI = -2.95 to 0.08; p = 0.06; I2 = 91%). All-cause dropout rates were not significantly different between groups.
Conclusion: Limited and heterogenous evidence suggests that short-term BWLT is well accepted, has a large treatment effect on post-TBI depressive symptoms, and may have a moderate treatment effect on post-TBI sleep disturbance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blue-wavelength light therapy for post-traumatic brain injury sleepiness, sleep disturbance, depression, and fatigue: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 4;16(2):e0246172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246172. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33539446 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Psychological therapies for treatment-resistant depression in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 14;5(5):CD010558. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010558.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29761488 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Educational interventions for the management of cancer-related fatigue in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 24;11(11):CD008144. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008144.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27883365 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapy of traumatic brain injury by modern agents and traditional Chinese medicine.Chin Med. 2023 Mar 11;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00731-x. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36906602 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18: 56–87. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30415-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

