Novel bridge multi-species ELISA for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
- PMID: 36202252
- PMCID: PMC9529351
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2022.113365
Novel bridge multi-species ELISA for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
Abstract
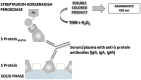
Considering the course of the current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, it is important to have serological tests for monitoring humoral immune response against SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. Herein we describe a novel bridge enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (b-ELISA) for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies detection in human and other species, employing recombinant Spike protein as a unique antigen, which is produced at high scale in insect larvae.
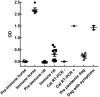
Methods: Eighty two human control sera/plasmas and 169 COVID-19 patients' sera/plasmas, confirmed by rRT-PCR, were analyzed by the b-ELISA assay. In addition, a total of 27 animal sera (5 horses, 13 rats, 2 cats and 7 dogs) were employed in order to evaluate the b-ELISA in other animal species.
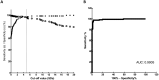
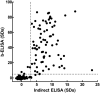
Results: Out of the 169 patient samples, 129 were positive for IgG anti-SARS-CoV-2 and 40 were negative when they were tested by ELISA COVIDAR® IgG. When a cut-off value of 5.0 SDs was established, 124 out of the 129 COVID-19 positive samples were also positive by our developed b-ELISA (sensitivity: 96.12%). Moreover, the test was able to evaluate the humoral immune response in animal models and also detected as positive a naturally infected cat and two dogs with symptoms, whose owners had suffered the COVID-19 disease.
Conclusion: The obtained results demonstrate that the method developed herein is versatile, as it is able to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in different animal species without the need to perform and optimize a new assay for each species.
Keywords: Bridge multi-species ELISA; Immune response; SARS-CoV-2; Spike protein.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Silvina Sonia Bombicino, Aldana Trabucchi, Alexandra Marisa Targovnik, Federico Javier Wolman, Leonardo Gabriel Alonso, Matías Fingermann, Silvina Noemí Valdez, and María Victoria Miranda are career researchers of the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas de Argentina (CONICET). Ignacio Smith and Gregorio Juan Mc callum are research fellows of CONICET. Adriana Victoria Sabljic is a research fellow of UBA. Juan Ignacio Marfía and Rubén Francisco Iacono belong to the career of Professional Support of CONICET. All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

