Prevalence of potentially inappropriate prescribing in older adults in Central and Eastern Europe: a systematic review and synthesis without meta-analysis
- PMID: 36202826
- PMCID: PMC9537527
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19860-8
Prevalence of potentially inappropriate prescribing in older adults in Central and Eastern Europe: a systematic review and synthesis without meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Prevalence of potentially inappropriate prescribing in older adults in Central and Eastern Europe: a systematic review and synthesis without meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 9;12(1):21304. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25155-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36494451 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
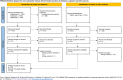
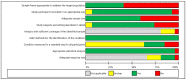
We aimed to systematically review the prevalence of potentially inappropriate prescribing (PIP) in older adults in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) in all care settings. We searched Embase and MEDLINE (up to June 2019) and checked the reference lists of the included studies and relevant reviews. Eligible studies used validated explicit or implicit tools to assess the PIP prevalence in older adults in CEE. All study designs were considered, except case‒control studies and case series. We assessed the risk of bias using the Joanna Briggs Institute Prevalence Critical Appraisal Tool and the certainty of evidence using the GRADE approach. Meta-analysis was inappropriate due to heterogeneity in the outcome measurements. Therefore, we used the synthesis without meta-analysis approach-summarizing effect estimates method. This review included twenty-seven studies with 139,693 participants. Most studies were cross-sectional and conducted in high-income countries. The data synthesis across 26 studies revealed the PIP prevalence: the median was 34.6%, the interquartile range was 25.9-63.2%, and the range was 6.5-95.8%. The certainty of this evidence was very low due to the risk of bias, imprecision, and inconsistency. These findings show that PIP is a prevalent issue in the CEE region. Further well-designed studies conducted across countries are needed to strengthen the existing evidence and increase the generalizability of findings.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mekonnen AB, Redley B, de Courten B, Manias E. Potentially inappropriate prescribing and its associations with health-related and system-related outcomes in hospitalised older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021;87:4150–4172. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hill-Taylor B, et al. Effectiveness of the STOPP/START (Screening Tool of Older Persons’ potentially inappropriate Prescriptions/Screening Tool to Alert doctors to the Right Treatment) criteria: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016;41:158–169. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12372. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

