Vitamin D status and determinants in Indian children and adolescents: a multicentre study
- PMID: 36202910
- PMCID: PMC9537341
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21279-0
Vitamin D status and determinants in Indian children and adolescents: a multicentre study
Abstract
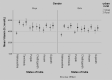
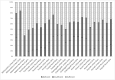
Studies performed on Indian children to assess vitamin-D status have been on small sample sizes, limited to specific geographical locations and used non-standard methods to measure 25(OH)D3. This multicentre study assessed 25(OH)D3 concentrations from dried blood spots (DBS) in 5-18-year-old Indian children and adolescents using a standardized protocol and identified factors contributing towards vitamin D deficiency. Cross-sectional, observational school-based study was conducted by multi-stage stratified random sampling. A city and nearby village were selected from 6 Indian states covering wide geographical areas. Demography, anthropometry, body-composition, dietary-intakes and DBS samples were collected. 25(OH)D3 was assessed from DBS using Liquid chromatography with tandem-mass spectrometry. Vitamin-D status was assessed in 2500 children; with additional data collected on a subset (n = 669) to assess predictors. Mean vitamin-D concentration was 45.8 ± 23.9 nmol/L, 36.8% of subjects had sufficient vitamin-D (> 50 nmol/L); rural subjects and boys had higher concentrations (p < 0.05). On regression analysis, younger age, female-gender, overweight and urban residence significantly contributed to deficiency. More than half the Indian children/adolescents were vitamin-D deficient or insufficient. Our study reinforces vitamin-D deficiency as a major public health problem and the need for supplementation, food fortification and educating the population as initiatives required to improve sufficiency status.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Misra M, Pacaud D, Petryk A, Collett-Solberg PF, Kappy M, Drug and Therapeutics Committee of the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: Review of current knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics. 2008;122(2):398–417. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-1894. - DOI - PubMed
-
- From Indian Academy of Pediatrics ‘Guideline for Vitamin D and Calcium in Children’ Committee. Khadilkar A, et al. Prevention and treatment of vitamin D and calcium deficiency in children and adolescents: Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Guidelines. Indian Pediatr. 2017;54(7):567–573. doi: 10.1007/s13312-017-1070-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

