Effect of a single vectored thermal pulsation treatment of Meibomian gland dysfunction patients under controlled environmental conditions
- PMID: 36202938
- PMCID: PMC9537290
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-20994-y
Effect of a single vectored thermal pulsation treatment of Meibomian gland dysfunction patients under controlled environmental conditions
Abstract
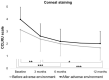
To assess the prophylactic effect of LipiFlow treatment in Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) patients exposed to an adverse environmental humidity. MGD patients were exposed to normal (23 °C; 50% relative humidity; 30 min) and adverse (23 °C; 10% relative humidity; 2 h) controlled environments consecutively during baseline and follow-up visits (3, 6, and 12 months) after a single LipiFlow treatment. Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI), lipid layer thickness (LLT), fluorescein tear break-up time (TBUT), corneal and conjunctival staining, change in dry eye symptoms questionnaire (CDES-Q), and Meibomian gland yielding liquid secretion (MGYLS), were assessed. Linear mixed-effects and cumulative logit mixed models were fitted to assess the effect of the LipiFlow treatment over time and within the controlled environments. Seventeen females and 4 males (59.6 ± 9.4 years) completed the study. LLT and TBUT did not vary significantly (p > 0.05) after LipiFlow treatment. OSDI, corneal and conjunctival staining, and MGYLS scores were improved (p ≤ 0.01) 12 months after treatment. After the adverse exposure, corneal staining increased at all visits (p = 0.01), and there was no significant improvement in CDES-Q scores after LipiFlow treatment (p ≥ 0.07). One LipiFlow treatment improved objective and subjective outcomes in MGD disease for at least one year. Further studies are needed to support that LipiFlow might also help as an adjuvant to avoid acute flares against an adverse environmental humidity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety evaluation of a single thermal pulsation system treatment (Lipiflow®) on meibomian gland dysfunction: a randomized controlled clinical trial.Int Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr;43(4):1175-1184. doi: 10.1007/s10792-022-02516-x. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Int Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36112256 Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative Management of MGD with Vectored Thermal Pulsation before Cataract Surgery: A Prospective, Controlled Clinical Trial.Semin Ophthalmol. 2021 Feb 17;36(1-2):2-8. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2021.1881567. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Semin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33587674 Clinical Trial.
-
Is a thermal pulsation system (LipiFlow) effective as a standalone treatment for meibomian gland dysfunction and dry eye? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2025 May 10;17:25158414251338775. doi: 10.1177/25158414251338775. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40352434 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of a vectored thermal pulsation system (Lipiflow®) in the treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022 Jan;260(1):25-39. doi: 10.1007/s00417-021-05363-1. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34374808
-
Which treatment works better for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: LipiFlow or intense pulsed light? A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2025 Jun;53:104630. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2025.104630. Epub 2025 May 11. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2025. PMID: 40360035
Cited by
-
Vectored Thermal Pulsation as a Treatment for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: A Review Spanning 15 Years.Ophthalmol Ther. 2024 Aug;13(8):2083-2123. doi: 10.1007/s40123-024-00976-1. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Ophthalmol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38879718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The photothermal effect of intense pulsed light and LipiFlow in eyelid related ocular surface diseases: Meibomian gland dysfunction, Demodex and blepharitis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 28;10(13):e33852. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33852. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing clinical and molecular outcomes of prophylactic thermal pulsation therapy on ocular surface health following refractive surgery.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr;71(4):1508-1516. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_3361_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37026292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greiner JV. A single LipiFlow® thermal pulsation system treatment improves meibomian gland function and reduces dry eye symptoms for 9 months. Curr. Eye Res. 2012;37:272–278. - PubMed
-
- Freedman HL, Preston KL. Heat retention in varieties of warm compresses: A comparison between warm soaks, hard-boiled eggs and the re-heater. Ophthalmic Surg. 1989;20:846–848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

