Anti-hyperalgesic effects of photobiomodulation therapy (904 nm) on streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathy imply MAPK pathway and calcium dynamics modulation
- PMID: 36202956
- PMCID: PMC9537322
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19947-2
Anti-hyperalgesic effects of photobiomodulation therapy (904 nm) on streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathy imply MAPK pathway and calcium dynamics modulation
Abstract
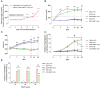
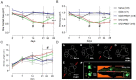
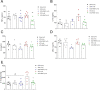
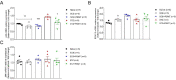
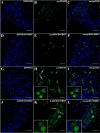
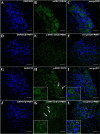
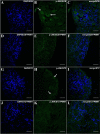
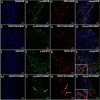
Several recent studies have established the efficacy of photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT) in painful clinical conditions. Diabetic neuropathy (DN) can be related to activating mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), such as p38, in the peripheral nerve. MAPK pathway is activated in response to extracellular stimuli, including interleukins TNF-α and IL-1β. We verified the pain relief potential of PBMT in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic neuropathic rats and its influence on the MAPK pathway regulation and calcium (Ca2+) dynamics. We then observed that PBMT applied to the L4-L5 dorsal root ganglion (DRG) region reduced the intensity of hyperalgesia, decreased TNF-α and IL-1β levels, and p38-MAPK mRNA expression in DRG of diabetic neuropathic rats. DN induced the activation of phosphorylated p38 (p-38) MAPK co-localized with TRPV1+ neurons; PBMT partially prevented p-38 activation. DN was related to an increase of p38-MAPK expression due to proinflammatory interleukins, and the PBMT (904 nm) treatment counteracted this condition. Also, the sensitization of DRG neurons by the hyperglycemic condition demonstrated during the Ca2+ dynamics was reduced by PBMT, contributing to its anti-hyperalgesic effects.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

