Determinants of food preparation and hygiene practices among caregivers of children under two in Western Kenya: a formative research study
- PMID: 36203140
- PMCID: PMC9535979
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-14259-6
Determinants of food preparation and hygiene practices among caregivers of children under two in Western Kenya: a formative research study
Abstract
Introduction: Diarrhea is a leading cause of child morbidity and mortality worldwide and is linked to early childhood stunting. Food contamination from improper preparation and hygiene practices is an important transmission pathway for exposure to enteric pathogens. Understanding the barriers and facilitators to hygienic food preparation can inform interventions to improve food hygiene. We explored food preparation and hygiene determinants including food-related handwashing habits, meal preparation, cooking practices, and food storage among caregivers of children under age two in Western Kenya.
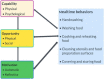
Methods: We used the Capabilities, Opportunities, and Motivations model for Behavior Change (COM-B) framework in tool development and analysis. We conducted 24 focus group discussions with mothers (N = 12), fathers (N = 6), and grandmothers (N = 6); 29 key informant interviews with community stakeholders including implementing partners and religious and community leaders; and 24 household observations. We mapped the qualitative and observational data onto the COM-B framework to understand caregivers' facilitators and barriers to food preparation and hygiene practices.
Results: Facilitators and barriers to food hygiene and preparation practices were found across the COM-B domains. Caregivers had the capability to wash their hands at critical times; wash, cook, and cover food; and clean and dry utensils. Barriers to food hygiene and preparation practices included lack of psychological capability, for instance, caregivers' lack of knowledge of critical times for handwashing, lack of perceived importance of washing some foods before eating, and not knowing the risks of storing food for more than four hours without refrigerating and reheating. Other barriers were opportunity-related, including lack of resources (soap, water, firewood) and an enabling environment (monetary decision-making power, social support). Competing priorities, socio-cultural norms, religion, and time constraints due to work hindered the practice of optimal food hygiene and preparation behaviors.
Conclusion: Food hygiene is an underexplored, but potentially critical, behavior to mitigate fecal pathogen exposure for young children. Our study revealed several knowledge and opportunity barriers that could be integrated into interventions to enhance food hygiene.
Keywords: Behavior change; COM-B; Food hygiene; Handwashing; Intervention development; Qualitative methods; WASH.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toward Complementary Food Hygiene Practices among Child Caregivers in Rural Malawi.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019 Aug;101(2):294-303. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0639. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019. PMID: 31237230 Free PMC article.
-
The Safe Start trial to assess the effect of an infant hygiene intervention on enteric infections and diarrhoea in low-income informal neighbourhoods of Kisumu, Kenya: a study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Dec 19;19(1):1066. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4657-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31856747 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Practices and Perspectives on Latrine Use, Child Feces Disposal, and Clean Play Environments in Western Kenya.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):1094-1103. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0389. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 32124727 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of clean birthing practices in low- and middle-income countries: a scoping review.BMC Public Health. 2020 May 1;20(1):602. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-8431-4. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32357872 Free PMC article.
-
Enablers and barriers to vaccine uptake and handwashing practices to prevent and control COVID-19 in Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania: a systematic review.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 27;12:1352787. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1352787. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38601496 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Handwashing among caregivers of young children in a protracted and complex refugee and immigration context: a mixed methods study on the Thai-Myanmar border.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 31;11:1099831. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1099831. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37583886 Free PMC article.
-
Hygiene Practices and Early Childhood Development in the East Asia-Pacific Region: A Cross-Sectional Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 4;20(4):2798. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20042798. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833497 Free PMC article.
-
Examining Safe Food-Handling Knowledge, Behaviour, and Related Psychological Constructs among Individuals at Higher Risk of Food Poisoning and the General Population.Foods. 2023 Sep 2;12(17):3297. doi: 10.3390/foods12173297. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37685229 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Hygiene Behaviours Among Child Caregivers in Rural Malawi Using Multilevel Logistic Models.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 May 20;22(5):801. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22050801. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40427914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with caregivers' food safety knowledge, behavior, perception of food safety control, and the nutrition status of under-5 children in Nigeria.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 14;24(1):2813. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20183-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39402544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . The global health observatory. 2022.
-
- Kinabo J, Mamiro P, Mwanri A, Bundala N, Msuya J, Ntwenya J, et al. Assessment of infant and young children feeding practices in Zanzibar using the process for the promotion of child feeding (ProPAN) tool. Ann Nutr Metab. 2013;63:35–36.
-
- Mills JE. The Impact of Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene on Key Health and Social Outcomes: Review of Evidence: Sanitation and Hygiene Applied Research for Equity (SHARE) 2016.
-
- WHO . Food Safety. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical