Effect of time-restricted eating on sex hormone levels in premenopausal and postmenopausal females
- PMID: 36203273
- PMCID: PMC9877115
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.23562
Effect of time-restricted eating on sex hormone levels in premenopausal and postmenopausal females
Abstract
Objective: Concerns have been raised regarding the impact of time-restricted eating (TRE) on sex hormones in females. This study examined how TRE affects sex steroids in premenopausal and postmenopausal females.
Methods: This is a secondary analysis of an 8-week TRE study (4- to 6-hour eating window) conducted in adults with obesity. Men and perimenopausal females were excluded. Females were classified into two groups based on menstrual status: premenopausal (n = 12) or postmenopausal (n = 11).
Results: After 8 weeks, body weight decreased in premenopausal females (-3% ± 2%) and postmenopausal females (-4% ± 2%) (main effect of time, p < 0.001), with no difference between groups (no group × time interaction). Circulating levels of testosterone, androstenedione, and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) did not change in either group (no group × time interaction). Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) concentrations decreased (p < 0.05) in premenopausal (-14% ± 32%) and postmenopausal females (-13% ± 34%; main effect of time, p = 0.03), with no difference between groups. Estradiol, estrone, and progesterone were measured only in postmenopausal females, and they remained unchanged.
Conclusions: In premenopausal females, androgens and SHBG remained unchanged during TRE, whereas DHEA decreased. In postmenopausal females, estrogens, progesterone, androgens, and SHBG did not change, but DHEA was reduced.
© 2022 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
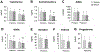
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

