Safety and Efficacy of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 in Multilevel Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion in a Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36203306
- PMCID: PMC9537859
- DOI: 10.14245/ns.2244464.232
Safety and Efficacy of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 in Multilevel Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion in a Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: This study is an investigator-initiated, prospective, randomized, controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the combined use of recombinant human BMP-2 (rhBMP-2) and a hydroxyapatite (HA) carrier in multilevel fusion in patients with adult spinal deformity (ASD).
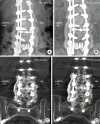
Methods: Thirty patients underwent posterolateral fusion for lumbar spinal deformities at 3 to 5 segments between L1 and S1. The patients received rhBMP-2+HA or HA on the left or right side of the transverse processes. They were followed up regularly at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. Fusion was defined according to the bone bridging on computed tomography scans. The fusion rate per segment was subanalyzed. Function and quality of life as well as pain in the lower back and lower extremities were evaluated.
Results: The union rate for the rhBMP-2+HA group was 100% at 6 and 12 months. The union rate for the HA group was 77.8% (21 of 27) at 6 months and 88.0% (22 of 25) at 12 months (p = 0.014 at 6 months; not significant at 12 months). All segments were fused at 6 and 12 months in the rhBMP-2+HA group (p < 0.001). In the HA group, 108 of 115 segments (93.5%) were fused at 6 months and 105 of 109 segments (96.3%) at 12 months. Other clinical parameters (visual analogue scale, 36-item Short Form Health Survey, and Scoliosis Research Society-22 scores) improved compared to baseline.
Conclusion: Combining rhBMP-2 and an HA carrier is a safe and effective method to achieve multilevel fusion in patients with ASD.
Keywords: Adult spinal deformity; Bone graft; Bone morphogenetic protein-2; Hydroxyapatite; Lumbar fusion; Posterolateral fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in posterolateral lumbar fusion: an open, active-controlled, randomized, multicenter trial.Spine J. 2017 Dec;17(12):1866-1874. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.06.023. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Spine J. 2017. PMID: 28652196 Clinical Trial.
-
Posterolateral lumbar intertransverse process spine arthrodesis with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2/hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate after laminectomy in the nonhuman primate.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999 Jun 15;24(12):1179-85. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199906150-00002. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999. PMID: 10382242
-
Posterolateral lumbar fusion using Escherichia coli-derived rhBMP-2/hydroxyapatite in the mini pig.Spine J. 2014 Dec 1;14(12):2959-67. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.06.007. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24937799
-
Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Safety of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Versus Autologous Iliac Crest Bone Graft in Lumbar Fusion: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020 Jun 15;45(12):E729-E741. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003372. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020. PMID: 31923133 Free PMC article.
-
Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 16: bone graft extenders and substitutes as an adjunct for lumbar fusion.J Neurosurg Spine. 2014 Jul;21(1):106-32. doi: 10.3171/2014.4.SPINE14325. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014. PMID: 24980593 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and radiological outcomes of titanium cage versus polyetheretherketone cage in lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Mar 12;48(1):295. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03453-w. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40075000
-
The Combined Effects of RhBMP-2 and Systemic RANKL Inhibitor in Patients With Bone Density Loss Undergoing Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Retrospective Observational Analysis With Propensity Score Matching.Neurospine. 2023 Dec;20(4):1186-1192. doi: 10.14245/ns.2346702.351. Epub 2023 Dec 31. Neurospine. 2023. PMID: 38171287 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic enhancement of spinal fusion in preclinical models using low-dose rhBMP-2 and stromal vascular fraction in an injectable hydrogel composite.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Dec 6;30:101379. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101379. eCollection 2025 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39759847 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive peptides and proteins for tissue repair: microenvironment modulation, rational delivery, and clinical potential.Mil Med Res. 2024 Dec 5;11(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00576-x. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39639374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selection of Optimal Lower Instrumented Vertebra for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgery.Neurospine. 2023 Sep;20(3):799-807. doi: 10.14245/ns.2346452.226. Epub 2023 Sep 30. Neurospine. 2023. PMID: 37798973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daniels AH, DePasse JM, Eberson CP, et al. Adult spinal deformity: contemporary treatment and patient outcomes. R I Med J (2013) 2015;98:32–41. - PubMed
-
- Frymoyer JW, Howe J, Kuhlmann D. The long-term effects of spinal fusion on the sacroiliac joints and ilium. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978:196–201. - PubMed
-
- Hu RW, Bohlman HH. Fracture at the iliac bone graft harvest site after fusion of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994:208–13. - PubMed
-
- Kurz LT, Garfin SR, Booth RE., Jr Harvesting autogenous iliac bone grafts. A review of complications and techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989;14:1324–31. - PubMed
-
- Younger EM, Chapman MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites. J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3:192–5. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

