Systematic review of locking solutions for non-tunneled hemodialysis catheters
- PMID: 36203330
- PMCID: PMC10092163
- DOI: 10.1111/hdi.13047
Systematic review of locking solutions for non-tunneled hemodialysis catheters
Abstract
Background: We conducted a systematic review of studies investigating lock solutions for use in non-tunneled hemodialysis catheters.
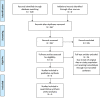
Methods: We searched PubMed and Cochrane databases from inception to June 11, 2021. Study inclusion criteria were: randomized trial or observational study, adults (>18 years), with acute kidney injury (AKI); and temporary non-tunneled catheters. We recorded bleeding events, catheter dysfunction and complications.
Results: Of 649 studies identified, 6 were included (4 randomized, 1 non-randomized trial, 1 retrospective cohort study; sample sizes 78-1496 patients). Citrate was compared to heparin in 4 studies, to saline in 1, and ethanol versus saline in 1. Event-free survival of non-tunneled catheters did not differ between groups. Catheter-related infections and adverse events were less frequent with citrate locks, but reached statistical significance in only two studies.
Conclusion: Existing data are too heterogeneous to enable recommending one type of catheter lock over any other for non-tunneled hemodialysis catheters.
Keywords: intensive care unit; locking solutions; non-tunneled hemodialysis catheters.
© 2022 The Authors. Hemodialysis International published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Hemodialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Schiffl H, Lang SM, Fischer R. Daily hemodialysis and the outcome of acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:305–10. - PubMed
-
- Investigators RRTS , Bellomo R, Cass A, Cole L, Finfer S, Gallagher M, et al. Intensity of continuous renal‐replacement therapy in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1627–38. - PubMed
-
- McGee DC, Gould MK. Preventing complications of central venous catheterization. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1123–33. - PubMed
-
- Siempos II, Kopterides P, Tsangaris I, Dimopoulou I, Armaganidis AE. Impact of catheter‐related bloodstream infections on the mortality of critically ill patients: a meta‐analysis. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:2283–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources