Radiomics-based nomogram as predictive model for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis receiving radiotherapy
- PMID: 36203419
- PMCID: PMC9530279
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.906498
Radiomics-based nomogram as predictive model for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis receiving radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: This study aims to establish and validate a predictive model based on radiomics features, clinical features, and radiation therapy (RT) dosimetric parameters for overall survival (OS) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated with RT for portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT).
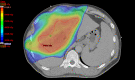
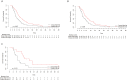
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 131 patients. Patients were randomly divided into the training (n = 105) and validation (n = 26) cohorts. The clinical target volume was contoured on pre-RT computed tomography images and 48 textural features were extracted. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression was used to determine the radiomics score (rad-score). A nomogram based on rad-score, clinical features, and dosimetric parameters was developed using the results of multivariate regression analysis. The predictive nomogram was evaluated using Harrell's concordance index (C-index), area under the curve (AUC), and calibration curve.
Results: Two radiomics features were extracted to calculate the rad-score for the prediction of OS. The radiomics-based nomogram had better performance than the clinical nomogram for the prediction of OS, with a C-index of 0.73 (95% CI, 0.67-0.79) and an AUC of 0.71 (95% CI, 0.62-0.79). The predictive accuracy was assessed by a calibration curve.
Conclusion: The radiomics-based predictive model significantly improved OS prediction in HCC patients treated with RT for PVTT.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; portal vein tumor thrombosis; predictive model; radiation therapy; radiomics.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Wang, Chen, Lin, Chang, Tai, Hsu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CT-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of survival after transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus.Eur Radiol. 2023 Dec;33(12):8715-8726. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09830-7. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37436507
-
Preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography-based radiomics model for overall survival prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 21;28(31):4376-4389. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4376. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36159012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development of a novel combined nomogram model integrating Rad-score, age and ECOG to predict the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Aug;13(4):1889-1897. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-548. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36092317 Free PMC article.
-
A radiomics nomogram for the prediction of overall survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Nov 16;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00360-9. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33198809 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A CT-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of focal nodular hyperplasia from hepatocellular carcinoma in the non-cirrhotic liver.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Feb 24;20(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00297-z. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32093786 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and verification of a nomogram for predicting portal vein tumor thrombosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Dec 15;16(12):7511-7520. doi: 10.62347/PLQF5135. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39822560 Free PMC article.
-
Predictability of clinical outcomes after external beam radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma according to tumor marker dynamics.PLoS One. 2025 May 20;20(5):e0323450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323450. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40392828 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of MRI-based radiomics in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 6;15:1420599. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1420599. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39980543 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence models for detecting the pterygium that requires surgical treatment based on anterior segment images.Front Neurosci. 2022 Dec 20;16:1084118. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1084118. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36605553 Free PMC article.
-
CT-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of survival after transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus.Eur Radiol. 2023 Dec;33(12):8715-8726. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09830-7. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37436507
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

