Electrochemotherapy for the treatment of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: The INSPECT experience (2008-2020)
- PMID: 36203425
- PMCID: PMC9531998
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.951662
Electrochemotherapy for the treatment of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: The INSPECT experience (2008-2020)
Abstract
Introduction: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is a frequent skin cancer with a high risk of recurrence characterized by tumor infiltration and, in advanced cases, a poor prognosis. ECT (electrochemotherapy) is an alternative treatment option for locally advanced or recurrent cSCC that is unsuitable for surgical resection. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the data in the InspECT (International Network for Sharing Practice on ECT) registry of the referral centers and to clarify the indications for the use of ECT as a treatment modality for cSCC.
Materials and methods: Patients with primary, recurrent or locally advanced cSCC from 18 European centers were included. They underwent at least one ECT session with bleomycin between February 2008 and November 2020, which was performed following the European Standard Operating Procedures.
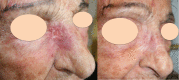
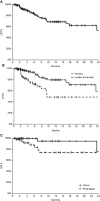
Results: The analysis included 162 patients (mean age of 80 years; median, 1 lesion/patient). Side effects were mainly local and mild (hyperpigmentation, 11%; ulceration, 11%; suppuration, 4%). The response to treatment per patient was 62% complete and 21% partial. In the multivariate model, intravenous drug administration and small tumor size showed a significant association with a positive outcome (objective response). One-year local progression-free survival was significantly better (p<0.001) in patients with primary tumors (80% (95% C.I. 70%-90%) than in patients with locally advanced disease (49% (95% C.I. 30%-68%).
Conclusion: In the present study, ECT showed antitumor activity and a favorable safety profile in patients with complex cSCC for whom there was no widely accepted standard of care. Better results were obtained in primary and small tumors (<3 cm) using intravenous bleomycin administration.
Keywords: cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma; electrochemotherapy; inspect; local treatment; skin cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Bertino, Groselj, Campana, Kunte, Schepler, Gehl, Muir, Clover, Quaglino, Kis, Mascherini, Bisase, Pecorari, Bechara, Matteucci, Odili, Russano, Orlando, Pritchard-Jones, Moir, Mowatt, Silvestri, Seccia, Saxinger, de Terlizzi and Sersa.
Conflict of interest statement
FT is an IGEA employer. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fania L, Massone C, Cusano F, Fantini F, Dellambra E, Samela T, et al. Integrated care pathways and the hub-and-spoke model for the management of non-melanoma skin cancer: A proposal of the Italian association of hospital dermatologists (ADOI). Dermatol Rep (2021) 13:9278. doi: 10.4081/dr.2021.9278 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

