Network Toxicology Guided Mechanism Study on the Association between Thyroid Function and Exposures to Polychlorinated Biphenyls Mixture
- PMID: 36203481
- PMCID: PMC9532094
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2394398
Network Toxicology Guided Mechanism Study on the Association between Thyroid Function and Exposures to Polychlorinated Biphenyls Mixture
Abstract
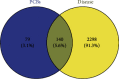
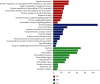
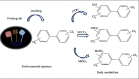
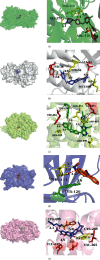
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent and highly toxic pollutants, which can accumulate in organisms and produce toxic effects, especially damaging the function of thyroid hormones. So far, the molecular mechanism of PCBs mixture and their metabolites interfering with thyroid hormones has not been studied thoroughly except for individual compounds. In this study, PubMed, Web of Science, and STITCH databases were used to search PCBs and their corresponding target proteins. The intersection of PCBs and thyroid hormone dysfunction target proteins was obtained from GeneCards. The "compounds-targets-pathways" network was constructed by Cytoscape software. And KEGG and Go analyses were performed for key targets. Finally, molecular docking was used to verify the binding effect. Four major active components, five key targets, and 10 kernel pathways were successfully screened by constructing the network. Functional enrichment analysis showed that the interference was mediated by cancer, proteoglycans, PI3K-Akt, thyroid hormone, and FoxO signaling pathways. The molecular docking results showed that the binding energies were less than -5 kcal·mol-1. PCBs and their metabolites may act on the key targets of MAPK3, MAPK1, RXRA, PIK3R1, and TP53. The toxic effect of sulfated and methyl sulfone PCBs is greater. The method of screening targets based on the simultaneous action of multiple PCBs can provide a reference for other research. The targets were not found in previous metabolite toxicity studies. It also provides a bridge for the toxic effects and experimental research of PCBs and their metabolites in the future.
Copyright © 2022 Chunxia Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Combining Network Pharmacology with Molecular Docking for Mechanistic Research on Thyroid Dysfunction Caused by Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Their Metabolites.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Nov 17;2021:2961747. doi: 10.1155/2021/2961747. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34840968 Free PMC article.
-
Xiao-Luo-Wan treats propylthiouracil-induced goiter with hypothyroidism in rats through the PI3K-AKT/RAS pathways based on UPLC/MS and network pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 May 10;289:115045. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115045. Epub 2022 Jan 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35101570
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
The Duisburg birth cohort study: influence of the prenatal exposure to PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs on thyroid hormone status in newborns and neurodevelopment of infants until the age of 24 months.Mutat Res. 2008 Jul-Aug;659(1-2):83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Nov 12. Mutat Res. 2008. PMID: 18093869 Review.
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implications for risk assessment.Crit Rev Toxicol. 1994;24(2):87-149. doi: 10.3109/10408449409049308. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1994. PMID: 8037844 Review.
Cited by
-
Network Toxicology and Molecular Docking Analysis of Tetracycline-Induced Acute Pancreatitis: Unveiling Core Mechanisms and Targets.Toxics. 2024 Dec 21;12(12):929. doi: 10.3390/toxics12120929. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39771144 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Carcinoma: A Review for 25 Years of Environmental Risk Factors Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;14(24):6172. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246172. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of polychlorinated biphenyls in breast cancer: insights from network toxicology and molecular docking approaches.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 13;16:1604993. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1604993. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40584614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng J., He C. T., Chen S. J., et al. Disruption of thyroid hormone (TH) levels and TH-regulated gene expression by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and hydroxylated PCBs in e-waste recycling workers. Environment International . 2017;102:138–144. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.02.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yao X. F. Southwest University of Science and Technology; 2016. The Study on Technique for Thyroid Hormone Signaling Disruption of Emerging Pollutants.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

