An explanatory model of temperature influence on flowering through whole-plant accumulation of FLOWERING LOCUS T in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 36203490
- PMCID: PMC9534314
- DOI: 10.1093/insilicoplants/diz006
An explanatory model of temperature influence on flowering through whole-plant accumulation of FLOWERING LOCUS T in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
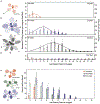
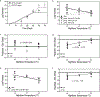
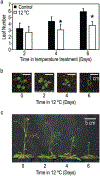
We assessed mechanistic temperature influence on flowering by incorporating temperature-responsive flowering mechanisms across developmental age into an existing model. Temperature influences the leaf production rate as well as expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), a photoperiodic flowering regulator that is expressed in leaves. The Arabidopsis Framework Model incorporated temperature influence on leaf growth but ignored the consequences of leaf growth on and direct temperature influence of FT expression. We measured FT production in differently aged leaves and modified the model, adding mechanistic temperature influence on FT transcription, and causing whole-plant FT to accumulate with leaf growth. Our simulations suggest that in long days, the developmental stage (leaf number) at which the reproductive transition occurs is influenced by day length and temperature through FT, while temperature influences the rate of leaf production and the time (in days) the transition occurs. Further, we demonstrate that FT is mainly produced in the first 10 leaves in the Columbia (Col-0) accession, and that FT accumulation alone cannot explain flowering in conditions in which flowering is delayed. Our simulations supported our hypotheses that: (i) temperature regulation of FT, accumulated with leaf growth, is a component of thermal time, and (ii) incorporating mechanistic temperature regulation of FT can improve model predictions when temperatures change over time.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; Arabidopsis thaliana; FT; Framework Model; crop simulation model; flowering time; mathematical model; phenology; photoperiodic flowering; thermal time.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Abe M, Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Daimon Y, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda Y, Ichinoki H, Notaguchi M, Goto K, Araki T. 2005. FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309:1052–1056. - PubMed
-
- Amasino R 2010. Seasonal and developmental timing of flowering. The Plant Journal 61:1001–1013. - PubMed
-
- Asseng S, Ewert F, Rosenzweig C, Jones JW, Hatfield JL, Ruane AC, Boote KJ, Thorburn PJ, Rötter RP, Cammarano D, Brisson N, Basso B, Martre P, Aggarwal PK, Angulo C, Bertuzzi P, Biernath C, Challinor AJ, Doltra J, Gayler S, Goldberg R, Grant R, Heng L, Hooker J, Hunt LA, Ingwersen J, Izaurralde RC, Kersebaum KC, Müller C, Naresh Kumar S, Nendel C, O’Leary G, Olesen JE, Osborne TM, Palosuo T, Priesack E, Ripoche D, Semenov MA, Shcherbak I, Steduto P, Stöckle C, Stratonovitch P, Streck T, Supit I, Tao F, Travasso M, Waha K, Wallach D, White JW, Williams JR, Wolf J. 2013. Uncertainty in simulating wheat yields under climate change. Nature Climate Change 3:827–832.
-
- Blázquez MA, Ahn JH, Weigel D. 2003. A thermosensory pathway controlling flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature Genetics 33:168–171. - PubMed
-
- Boote KJ, Jones JW, White JW, Asseng S, Lizaso JI. 2013. Putting mechanisms into crop production models. Plant, Cell & Environment 36:1658–1672. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
