A soybean sodium/hydrogen exchanger GmNHX6 confers plant alkaline salt tolerance by regulating Na+/K+ homeostasis
- PMID: 36204047
- PMCID: PMC9531905
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.938635
A soybean sodium/hydrogen exchanger GmNHX6 confers plant alkaline salt tolerance by regulating Na+/K+ homeostasis
Abstract
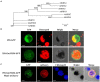
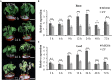
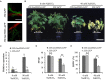
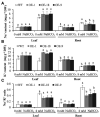
Alkaline soil has a high pH due to carbonate salts and usually causes more detrimental effects on crop growth than saline soil. Sodium hydrogen exchangers (NHXs) are pivotal regulators of cellular Na+/K+ and pH homeostasis, which is essential for salt tolerance; however, their role in alkaline salt tolerance is largely unknown. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the function of a soybean NHX gene, GmNHX6, in plant response to alkaline salt stress. GmNHX6 encodes a Golgi-localized sodium/hydrogen exchanger, and its transcript abundance is more upregulated in alkaline salt tolerant soybean variety in response to NaHCO3 stress. Ectopic expression of GmNHX6 in Arabidopsis enhanced alkaline salt tolerance by maintaining high K+ content and low Na+/K+ ratio. Overexpression of GmNHX6 also improved soybean tolerance to alkaline salt stress. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter region of NHX6 is associated with the alkaline salt tolerance in soybean germplasm. A superior promoter of GmNHX6 was isolated from an alkaline salt tolerant soybean variety, which showed stronger activity than the promoter from an alkaline salt sensitive soybean variety in response to alkali stress, by luciferase transient expression assays. Our results suggested soybean NHX6 gene plays an important role in plant tolerance to alkaline salt stress.
Keywords: abiotic stress; alkaline salt tolerance; natural variation; promoter; sodium bicarbonate; sodium hydrogen exchanger; soybean.
Copyright © 2022 Jin, An, Xu, Chen, Pan, Zhao, Wang, Gai and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter gene from date palm (PdNHX6) confers enhanced salt tolerance response in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Rep. 2020 Aug;39(8):1079-1093. doi: 10.1007/s00299-020-02549-5. Epub 2020 May 7. Plant Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32382811
-
A Glycine max sodium/hydrogen exchanger enhances salt tolerance through maintaining higher Na+ efflux rate and K+/Na+ ratio in Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Nov 5;19(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2084-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31690290 Free PMC article.
-
A Golgi-Localized Sodium/Hydrogen Exchanger Positively Regulates Salt Tolerance by Maintaining Higher K+/Na+ Ratio in Soybean.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 9;12:638340. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.638340. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33767722 Free PMC article.
-
Unfolding molecular switches for salt stress resilience in soybean: recent advances and prospects for salt-tolerant smart plant production.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Apr 19;14:1162014. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1162014. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37152141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the regulation of wild soybean tolerance to salt-alkaline stress.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 19;13:1002302. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1002302. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36340388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Twenty years of mining salt tolerance genes in soybean.Mol Breed. 2023 May 23;43(6):45. doi: 10.1007/s11032-023-01383-3. eCollection 2023 Jun. Mol Breed. 2023. PMID: 37313223 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Expression Network Analysis of the Transcriptome Identified Hub Genes and Pathways Responding to Saline-Alkaline Stress in Sorghum bicolor L.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 27;24(23):16831. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316831. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069156 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of drought and salinity tolerance potentials of different soybean genotypes based upon physiological, biochemical, and genetic indicators.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Dec 6;15:1466363. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1466363. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39711599 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the SiNHX Gene Family in Foxtail Millet (Setaria Italica) and Functional Characterization of SiNHX7 in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7139. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157139. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806288 Free PMC article.
-
Iron oxide nanoparticles enhance alkaline stress resilience in bell pepper by modulating photosynthetic capacity, membrane integrity, carbohydrate metabolism, and cellular antioxidant defense.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Feb 10;25(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06180-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39924529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Harrasi I., Jana G. A., Patankar H. V., Al-Yahyai R., Rajappa S., Kumar P. P., et al. (2020). A novel tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter gene from date palm (PdNHX6) confers enhanced salt tolerance response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 39, 1079–1093. doi: 10.1007/s00299-020-02549-5, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barragán V., Leidi E. O., Andrés Z., Rubio L., De Luca A., Fernández J. A., et al. (2012). Ion exchangers NHX1 and NHX2 mediate active potassium uptake into vacuoles to regulate cell turgor and stomatal function in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 1127–1142. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.095273, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

