Application of herbs and active ingredients ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease under the guidance of traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 36204095
- PMCID: PMC9530134
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1000727
Application of herbs and active ingredients ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease under the guidance of traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
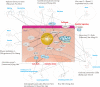
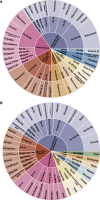
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a global health problem, and its prevalence has been on the rise in recent years. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) contains a wealth of therapeutic resources and has been in use for thousands of years regarding the prevention of liver disease and has been shown to be effective in the treatment of NAFLD in China. but the molecular mechanisms behind it have not been elucidated. In this article, we have updated and summarized the research and evidence concerning herbs and their active ingredients for the treatment in vivo and vitro models of NAFLD or NASH, by searching PubMed, Web of Science and SciFinder databases. In particular, we have found that most of the herbs and active ingredients reported so far have the effect of clearing heat and dispelling dampness, which is consistent with the concept of dampness-heat syndrome, in TCM theory. we have attempted to establish the TCM theory and modern pharmacological mechanisms links between herbs and monomers according to their TCM efficacy, experiment models, targets of modulation and amelioration of NAFLD pathology. Thus, we provide ideas and perspectives for further exploration of the pathogenesis of NAFLD and herbal therapy, helping to further the scientific connotation of TCM theories and promote the modernization of TCM.
Keywords: Dampness-heat syndrome; TCM; herbs; ingredients; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Zhang, You, Wang, Wang, Wang, Kong, Gao and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, et al. . The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American gastroenterological association, American association for the study of liver diseases, and American college of gastroenterology. Gastroenterology (2012) 142(7):1592–609. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

